In the quest for cleaner energy, Turkey is harnessing the power of advanced decision-making tools to pinpoint the best locations for wind energy investments. A recent study published in the journal *Nature Scientific Reports* introduces a novel framework that combines Geographic Information Systems (GIS) with the Neutrosophic-VIKOR method, offering a more nuanced approach to wind energy planning.
The research, led by Hasan Eroğlu from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at Recep Tayyip Erdoğan University, addresses a critical challenge in renewable energy planning: the complex interplay of technical, spatial, and economic factors, all of which are fraught with uncertainty. “Identifying optimal regions for wind energy investment is a multifaceted problem,” Eroğlu explains. “Our model integrates expert judgment and spatial analysis within an uncertainty-aware framework, providing a more robust tool for decision-makers.”
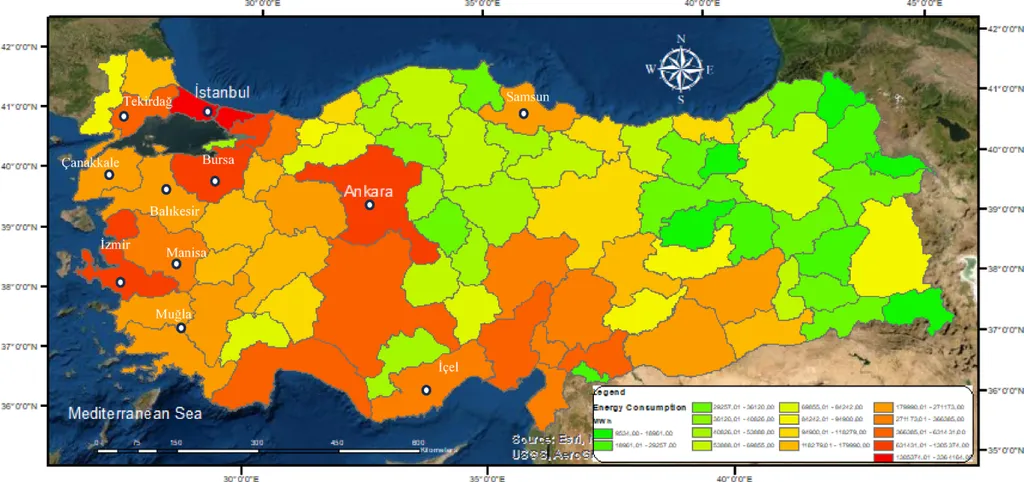
The study evaluates five core criteria: wind potential, land cost, energy consumption based on population density, the presence of existing wind farms, and expert judgment. By using Single-Valued Neutrosophic linguistic scales to represent expert input and a similarity-based weighting method to determine the relative influence of each expert, the model generates a Priority Index (PI). This index highlights Balıkesir, Çanakkale, and İzmir as the top three investment regions due to their favorable wind characteristics and energy demand. Istanbul and Samsun also rank highly, supported by existing infrastructure and consumption levels.
The commercial implications of this research are significant. For investors, the framework offers a data-driven approach to identifying high-potential regions, reducing the risks associated with wind energy investments. For policymakers, it provides a replicable tool for supporting national wind energy planning, ensuring a more efficient and balanced development of renewable energy resources.
“This framework not only addresses existing methodological gaps but also provides actionable insights for investors and policymakers,” Eroğlu notes. “By combining expert-based neutrosophic modeling with spatial analysis, we can support more informed decision-making in the renewable energy sector.”
The study’s innovative approach could shape future developments in renewable energy planning, offering a more comprehensive and uncertainty-aware tool for identifying optimal investment regions. As the world continues to shift towards cleaner energy sources, such frameworks will be crucial in ensuring that investments are made in the most strategic and impactful locations.