In the rapidly evolving energy landscape, the integration of renewable sources into power systems has introduced a new layer of complexity, particularly in the interplay between distribution networks and Virtual Power Plants (VPPs). A groundbreaking study led by Wen-Bin Hao of the State Grid Sichuan Electric Power Company Chengdu Power Supply Company has proposed a novel methodology to tackle this challenge, potentially reshaping how we approach power system planning and operation.
The research, published in the journal “Energy Informatics,” introduces a hybrid methodology that combines a multi-dimensional evaluation index system with a dynamic weighting approach. This approach leverages the entropy method for initial weight generation and Long Short-TTerm Memory (LSTM) networks for optimization. “The entropy method helps us establish a baseline, while LSTM’s ability to process sequential data and capture temporal dependencies allows us to dynamically adjust the weights of evaluation indicators based on historical operational patterns,” Hao explains.
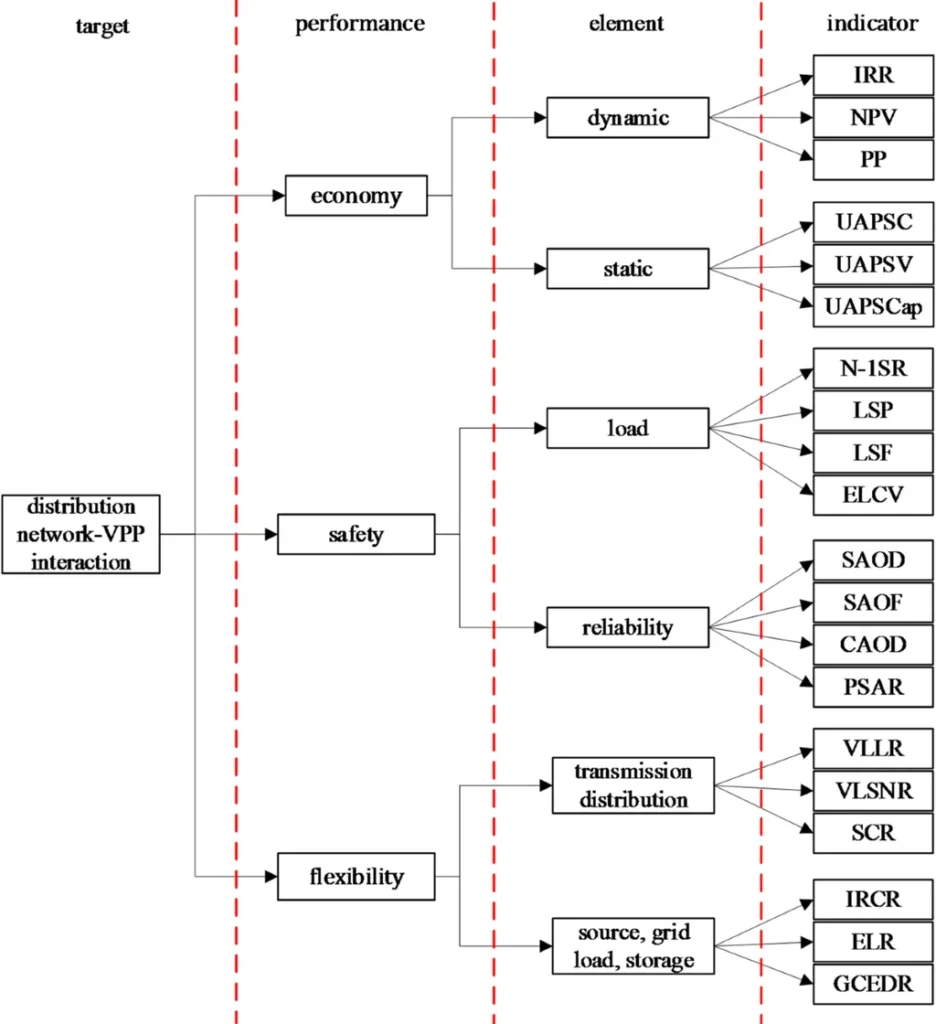
The evaluation index system covers economic, safety, and flexibility dimensions, with specific indicators designed to capture the complex interdependencies and dynamic characteristics of distribution network-VPP interactions. The LSTM network, a type of recurrent neural network, enhances the accuracy and adaptability of the assessment by learning from historical data.
The implementation results are promising, with a mean squared error (MSE) of 0.0012, a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.0056, and a weighted relative correctness (WRC) of 96.2%. Testing using real-world operational data from a regional distribution network confirmed a 95.0% match with expert argumentation, highlighting the practical applicability and robustness of the methodology.
This study contributes significantly to the advancement of data-driven decision-making frameworks for power system planning and operation. As the energy sector strives towards integrating distributed energy resources and achieving carbon neutrality goals, such methodologies can provide valuable insights and enhance operational efficiency.
The commercial impacts of this research are substantial. By improving the accuracy and adaptability of power system assessments, energy companies can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance the reliability of their networks. This can lead to more efficient integration of renewable energy sources, ultimately benefiting both the environment and the bottom line.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the methodology proposed by Hao and his team could play a pivotal role in shaping future developments. By providing a robust framework for assessing distribution network-VPP interactions, it can help energy companies navigate the complexities of the modern energy landscape and make informed decisions that drive the transition towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future.