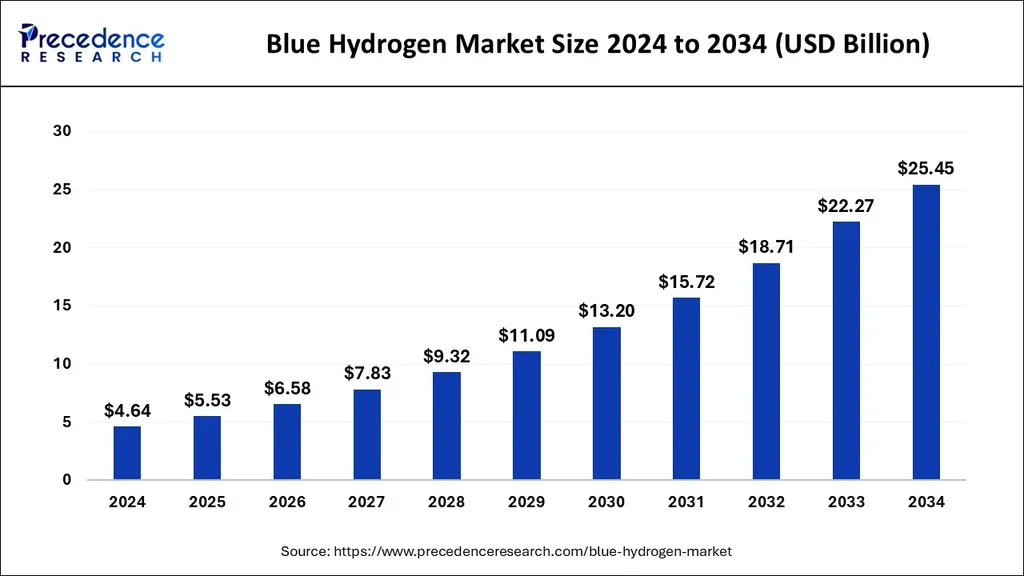
The global blue hydrogen market is at a crossroads, poised to reshape the energy landscape as it bridges the gap between fossil fuel-based and fully renewable hydrogen. In 2025, the market is projected to reach USD 2,511.31 million, a significant leap from USD 2,242.24 million in 2024, and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% through 2034. This growth is not merely a numerical trend but a testament to the strategic importance of blue hydrogen in the global push towards net-zero emissions.
Blue hydrogen, produced through steam methane reforming (SMR) or autothermal reforming (ATR) combined with carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), offers a lower-carbon alternative to traditional “grey” hydrogen. This positions it as a critical transition fuel, particularly in sectors such as refineries, ammonia production, steelmaking, long-haul transport, and power generation. The demand for hydrogen is expected to exceed 200 million tons annually by 2030, and blue hydrogen, with its cost competitiveness and lower carbon intensity compared to green hydrogen, is well-positioned to meet a significant portion of this demand.
The United States, Canada, Germany, the UK, Japan, and Saudi Arabia are at the forefront of developing blue hydrogen infrastructure. Major energy companies like Shell, BP, and Equinor are investing heavily in large-scale projects, underscoring the strategic importance of blue hydrogen in decarbonizing heavy industry and transport. The U.S. Department of Energy’s allocation of over USD 8 billion for regional clean hydrogen hubs further highlights the commitment to this technology.
The U.S. market, in particular, is rapidly emerging as a leader in blue hydrogen, driven by strong policy support, abundant natural gas reserves, and accelerated investments in CCUS infrastructure. The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 provides tax credits of up to USD 3 per kilogram of low-carbon hydrogen, making blue hydrogen financially competitive. Large-scale projects in Texas, Louisiana, and California are expected to produce over 1 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2030, with significant CO₂ capture capabilities.
Regionally, the market is diverse. North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are the largest contributors, with each region bringing unique advantages. North America benefits from abundant natural gas and strong policy support, while Europe is driven by ambitious climate policies and industrial demand. Asia-Pacific, with its rapid industrialization and energy needs, presents significant growth opportunities.
The implications of this growth are profound. Blue hydrogen offers a scalable and cost-effective solution that can pave the way for the long-term adoption of green hydrogen. It provides a bridge between the current fossil fuel-based energy system and a future powered by renewables. However, the success of blue hydrogen hinges on continued investment, technological advancements in carbon capture, and robust policy support.
As the global energy landscape evolves, the blue hydrogen market stands at a pivotal stage. It offers a viable path to decarbonization, but it also faces challenges and competition from green hydrogen. The next decade will be crucial in determining the role of blue hydrogen in the clean energy transition. The choices made today will shape the energy markets of tomorrow, influencing everything from industrial processes to transportation and power generation. The blue hydrogen market is not just growing; it is reshaping the future of energy.