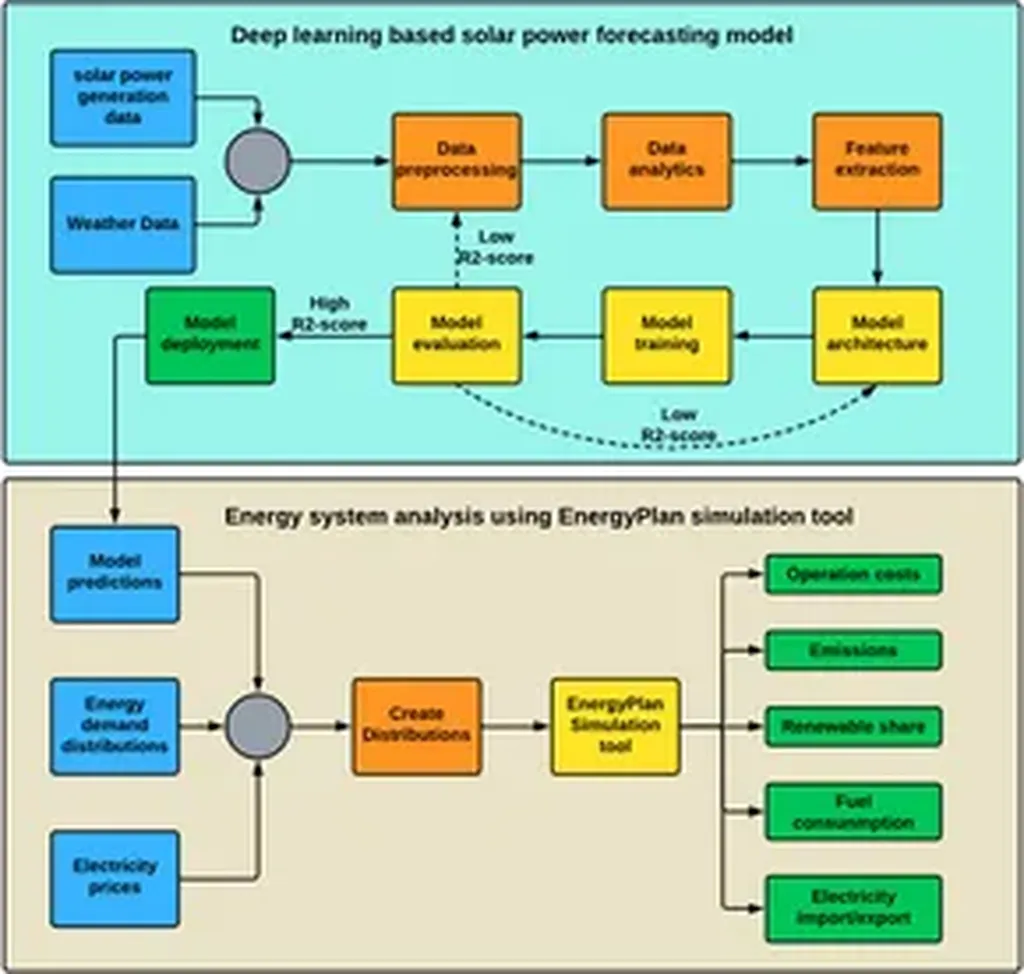
In the rapidly evolving landscape of renewable energy, integrating solar power into the grid efficiently and accurately is a persistent challenge. A novel approach developed by researchers, including lead author Ayesha Siddiqa, aims to revolutionize solar power forecasting, making it more accurate and interpretable. Published in the open-access journal “PLOS ONE,” the study introduces a two-stage hybrid framework that combines deep learning with generative AI to enhance solar power predictions.
The SolarTrans model, as it’s called, leverages a lightweight Transformer-based encoder-decoder architecture to predict short-term DC power outputs. By analyzing multivariate data—including irradiance, ambient and module temperatures, and temporal features—the model delivers impressive results. On datasets from two PV plants, SolarTrans achieved a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) as low as 0.0782 and an R2 score as high as 0.9692, indicating high predictive accuracy.
But accuracy alone isn’t enough. To make the model more practical for real-world applications, the researchers fine-tuned the Flan-T5 model to generate natural language explanations for the forecasts. This interpretability is crucial for energy sector professionals who need to understand the reasoning behind predictions to make informed decisions.
“Interpretability is key,” Siddiqa explains. “Energy professionals need to trust the model and understand its outputs to integrate solar power effectively into the grid.”
The implications for the energy sector are significant. Accurate and interpretable solar power forecasts can optimize grid management, reduce energy costs, and enhance the reliability of renewable energy sources. As the world shifts towards cleaner energy solutions, tools like SolarTrans could play a pivotal role in ensuring a stable and efficient energy infrastructure.
“This research is a step towards making solar power more predictable and reliable,” Siddiqa adds. “It’s about bridging the gap between advanced AI models and practical energy management.”
The study’s findings, published in “PLOS ONE,” highlight the potential of combining deep learning with generative AI to address real-world challenges. As the energy sector continues to evolve, such innovations could shape the future of renewable energy integration, making solar power a more viable and dependable source of energy.
In the broader context, this research underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration. By merging expertise from AI, energy, and natural language processing, the study demonstrates how cutting-edge technology can be harnessed to solve complex problems. As the energy sector continues to evolve, such innovations could shape the future of renewable energy integration, making solar power a more viable and dependable source of energy.