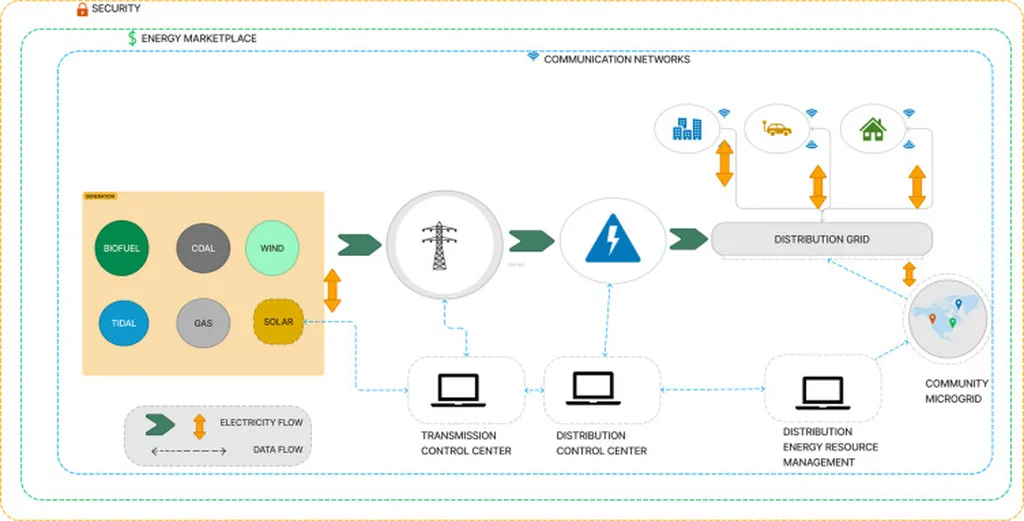
In the rapidly evolving energy landscape, distributed energy storage systems (DESSs) are emerging as key players in maintaining grid stability. A recent study published in the *International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems*, led by Tao Xu from the State Key Laboratory of Smart Power Distribution Equipment and System at Tianjin University, sheds light on how these systems can be more effectively integrated into the frequency regulation (FR) market. The research offers a comprehensive framework for distributed energy storage aggregation service providers (DSAPs) to incentivize DESS participation, potentially revolutionizing how energy markets operate.
Frequency regulation is crucial for maintaining the balance between electricity supply and demand, ensuring the grid operates smoothly. DESSs, which store energy from renewable sources and release it as needed, can play a pivotal role in this process. However, their participation in the FR market has been limited due to complexities in forecasting and optimizing their performance. Xu’s research addresses these challenges by proposing a two-pronged approach: day-ahead and intra-day market strategies.
In the day-ahead market, DSAPs predict the charging and discharging profiles of DESSs based on load estimation and bid according to a stepwise quotation strategy. The dispatching center then optimizes the scheduling plan with the goal of minimizing FR costs. “This approach ensures that DESSs are utilized efficiently, reducing overall costs and enhancing grid stability,” explains Xu.
The intra-day market strategy takes into account the differences between forecasted and real-time loading conditions. DSAPs aim to maximize net revenue by optimizing the capacity allocation and output strategy of DESSs. This dynamic approach allows for real-time adjustments, ensuring that DESSs can respond swiftly to changes in the grid’s needs.
The study’s case study demonstrates the effectiveness and economic benefits of DESS participation in the FR market. By providing a clear framework for DSAPs, the research paves the way for more widespread adoption of DESSs, potentially lowering costs and improving grid reliability.
The implications of this research are significant for the energy sector. As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the need for effective energy storage and grid regulation will only grow. Xu’s work offers a roadmap for integrating DESSs into the market, ensuring that these systems can contribute to a more stable and efficient grid.
“Our findings highlight the importance of a structured approach to DESS participation in the FR market,” says Xu. “By optimizing both day-ahead and intra-day strategies, we can unlock the full potential of these systems, benefiting both the grid and consumers.”
As the energy sector continues to evolve, research like Xu’s will be instrumental in shaping future developments. By providing a clear, actionable framework, this study could accelerate the adoption of DESSs, leading to a more resilient and efficient energy infrastructure. The publication of this research in the *International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems* underscores its significance and potential impact on the field.