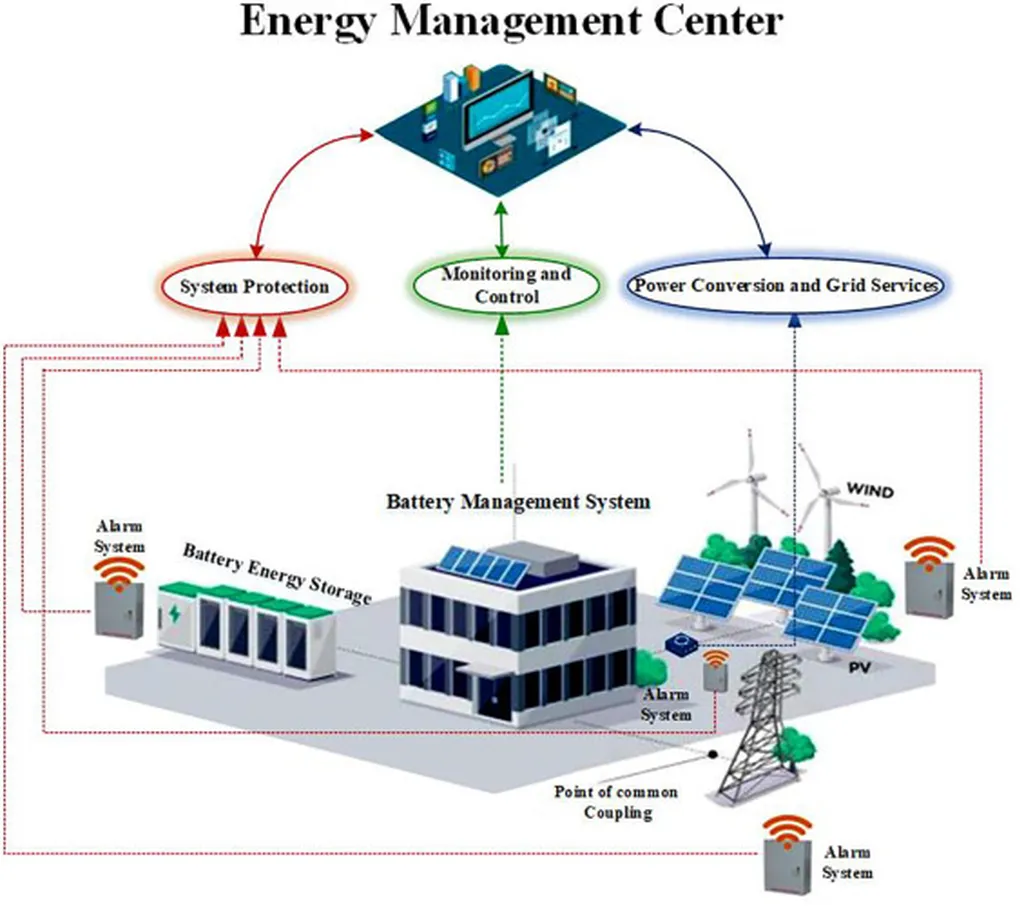
In the rapidly evolving energy sector, the integration of renewable energy sources and the optimization of energy storage systems are critical challenges. A recent study published in the journal *Energies*, titled “Bi-Level Optimal Operation Method for Regional Energy Storage Considering Dynamic Electricity Prices,” offers a novel approach to these issues. Led by Weilin Zhang of the State Grid Wenling Power Supply Company in China, the research introduces a dual-layer optimization method that could significantly impact how regional energy storage systems are operated, particularly in the context of dynamic electricity pricing.
The study addresses the growing influence of real-time electricity prices on load demand response, a crucial factor in modern energy markets. Zhang and his team proposed a method that not only considers dynamic electricity prices but also accounts for battery capacity degradation, a often-overlooked aspect in energy storage optimization. “The innovation lies in introducing user satisfaction and establishing real-time electricity price models based on fuzzy theory and consumer satisfaction,” Zhang explained. This approach makes dynamic electricity prices more realistic and practical, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of energy storage systems.
The dual-layer optimization model developed by Zhang’s team is designed to balance economic benefits with the longevity of energy storage batteries. By utilizing the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, the method efficiently optimizes charging and discharging strategies. This balance is crucial for the commercial viability of energy storage systems, as it ensures that economic gains are not achieved at the expense of battery lifespan.
Simulation results presented in the study highlight the potential impacts of different pricing models. Real-time electricity prices based on consumer satisfaction were found to increase load demand response resources, leading to a 73.7% improvement in the absorption of new energy sources. However, this came with a trade-off, reducing economic efficiency by 11.27%. On the other hand, real-time electricity prices based on fuzzy theory showed a weaker absorption of new energy sources, improving by only 36.4%, but achieved the best overall economic performance.
The findings of this research have significant implications for the energy sector. As the integration of renewable energy sources continues to grow, the need for efficient and cost-effective energy storage solutions becomes increasingly important. Zhang’s method offers a promising approach to optimizing regional energy storage systems, ensuring that they can effectively support the grid while maintaining economic viability.
“We hope that our research will contribute to the development of more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions,” Zhang said. “By considering both economic and technical factors, we can create systems that are not only beneficial for the environment but also commercially viable.”
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the insights provided by Zhang and his team could shape the future of regional energy storage and dynamic electricity pricing. The study, published in *Energies*, serves as a valuable resource for professionals and researchers seeking to advance the field of energy storage and optimize the integration of renewable energy sources.