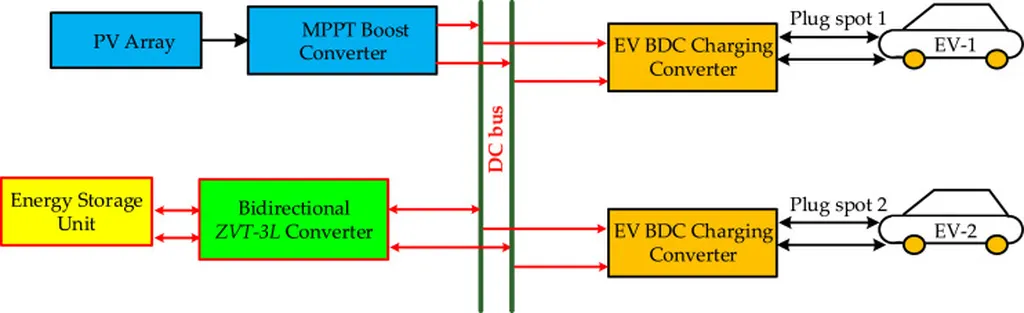
In the rapidly evolving world of electric vehicles (EVs), one of the critical challenges has been efficient battery charging and discharging. A recent study published in the journal “IEEE Access” titled “An Extended Voltage Gain Three-Level DC/DC Bidirectional Converter in an Electric Vehicle Traction System” offers a promising solution to this very issue. The lead author, Nalluri Ramya Sri from the School of Electrical Engineering at Vellore Institute of Technology in India, and her team have developed a novel DC/DC bidirectional converter that could significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of EV systems.
The research focuses on the increasing demand for DC/DC bidirectional converters in electric vehicle electrical systems. Unlike unidirectional converters, bidirectional converters can manage the flow of energy in both directions, which is crucial for EVs. “The demand for DC/DC bidirectional converters in electric vehicles is significantly higher than that for DC/DC unidirectional converters,” explains Ramya Sri. This is because EVs necessitate an increased voltage gain in DC/DC converters to coordinate the voltage levels of the battery and DC-link.
The proposed converter is a three-level bidirectional design that provides substantial voltage gain in both directions. What sets this converter apart is its simplicity and efficiency. It comprises just 13 components, making it a compact and cost-effective solution. Moreover, it minimizes voltage stress on switches in both directions, enhancing its durability and performance.
The converter’s effectiveness was validated through MATLAB simulations and OPAL-RT (OP5700) results for 2000W power in both directions. The charging and discharging procedure of a lithium-ion battery (48V, 75Ah) occurred via the constant voltage mode, demonstrating the converter’s practical applicability.
The implications of this research are substantial for the energy sector. As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation, the efficiency and reliability of EV systems become paramount. This extended voltage gain DC/DC bidirectional converter could play a pivotal role in advancing EV technology, making it more accessible and efficient.
The study’s findings could shape future developments in the field by providing a robust and efficient solution for battery charging and discharging in EVs. As Ramya Sri notes, “This converter structure is simple, comprising a fair total of 13 components.” This simplicity, combined with its high performance, makes it a promising candidate for commercial applications.
In conclusion, the research by Nalluri Ramya Sri and her team represents a significant step forward in EV technology. As the energy sector continues to evolve, such innovations will be crucial in driving the transition towards sustainable and efficient transportation solutions. The study was published in the journal “IEEE Access,” which translates to “Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Access,” a prestigious platform for cutting-edge research in electrical and electronics engineering.