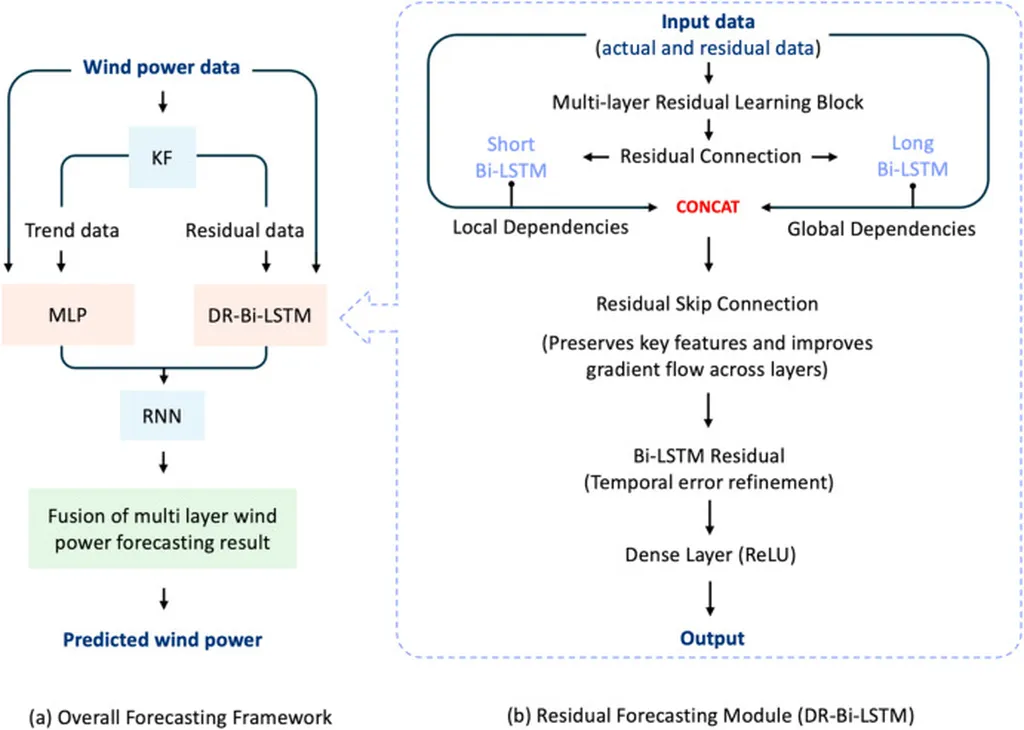
In the rapidly evolving landscape of renewable energy, wind power has emerged as a cornerstone, but its intermittent nature poses significant challenges for grid stability and operational efficiency. A recent study published in the *Gazi University Journal of Science*, led by Mehmet Yeşilbudak of Nevşehir Hacı Bektaş Veli University’s Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, delves into the critical role of wind power forecasting for very short-term and short-term horizons. The research offers a comprehensive review and assessment of existing forecasting methods, providing valuable insights for utilities, system operators, and researchers aiming to harness wind energy more effectively.
Wind power’s volatility can lead to operational headaches for grid managers, from frequency fluctuations to reserve capacity issues. Accurate forecasting is key to mitigating these challenges, enabling better resource allocation and reducing the need for costly backup power. Yeşilbudak’s study meticulously compares various forecasting models, evaluating them based on factors such as wind power plant properties, model inputs, data recording intervals, and forecast performance metrics.
“The intermittent nature of wind speed causes significant problems in system operations,” Yeşilbudak explains. “Our study highlights the importance of accurate wind power forecasts in alleviating these issues and improving the overall efficiency of wind energy integration into the grid.”
The research underscores the need for standardized evaluation criteria to ensure fair comparisons among different forecasting models. By identifying gaps and recommending best practices, the study paves the way for more reliable and efficient wind power forecasting techniques.
For the energy sector, the implications are substantial. Enhanced forecasting capabilities can lead to more stable grid operations, reduced energy costs, and increased reliance on renewable sources. As wind energy penetration continues to grow, the insights from this study will be instrumental in shaping future developments and ensuring a smoother transition to a more sustainable energy landscape.
Yeşilbudak’s work, published in the *Gazi University Journal of Science*, serves as a critical resource for stakeholders looking to optimize wind power integration and improve grid reliability. By addressing the challenges head-on, this research not only advances the field of wind energy forecasting but also contributes to the broader goal of achieving a more resilient and sustainable energy future.