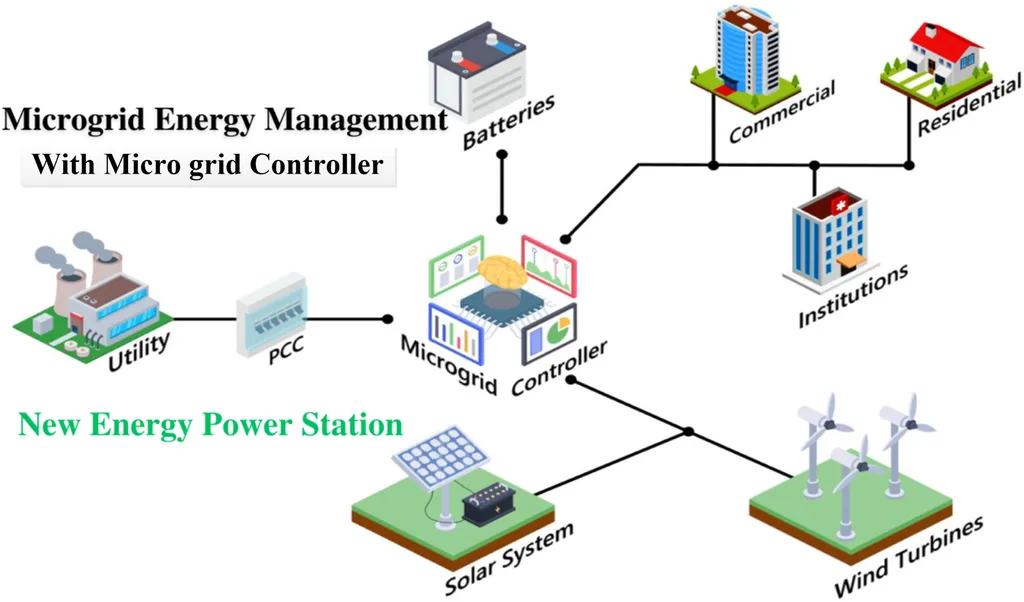
In the quest for more efficient and sustainable energy systems, researchers have made a significant stride in optimizing hybrid micro-grids. A recent study published in *Control and Information Technology* (Kongzhi Yu Xinxi Jishu) introduces a novel approach to configuring wind-solar-storage-load micro-grid systems, promising substantial energy savings and improved system flexibility.
Lead author ZHANG Jietian and his team tackled a critical challenge in the construction of energy internet: the capacity configuration of hybrid micro-grid systems. By accurately modeling the loss characteristics of these systems, the researchers aimed to reduce the overall loss of power electronic converters, a key component in micro-grid efficiency.
Traditional modeling methods often treat converter efficiency as a fixed value, but ZHANG’s team took a more nuanced approach. “We used a piecewise linear method to describe the variation characteristics of the converter efficiency with the output power,” ZHANG explained. This method provides a more accurate representation of the system’s behavior, leading to better optimization.
The study also considered the complementary nature of wind and solar energy, as well as the energy storage capabilities of centralized electric vehicle charging stations. This comprehensive approach improved the flexibility and reliability of the system configuration.
To optimize the energy storage configuration, the researchers employed a simulated annealing algorithm. This method helped them achieve a 36.68% reduction in system loss compared to general expert configurations. Moreover, when electric vehicles were used as energy storage devices, the overall system loss decreased by 9.30% compared to scenarios where electric vehicles were only used as loads.
The implications of this research are significant for the energy sector. As the world shifts towards renewable energy sources, efficient and flexible micro-grid systems will play a crucial role in ensuring stable and reliable power supply. ZHANG’s work could pave the way for more optimized and cost-effective energy solutions, benefiting both consumers and the environment.
“This research is a step forward in the development of smart energy systems,” ZHANG noted. “It demonstrates the potential of advanced modeling and optimization techniques in improving the efficiency of micro-grid systems.”
As the energy sector continues to evolve, studies like this one will be instrumental in shaping the future of power generation and distribution. By leveraging the unique characteristics of different energy sources and storage systems, researchers can develop more robust and efficient solutions for the challenges ahead.