In the rapidly evolving landscape of smart cities, where the integration of IoT devices and data-driven systems is revolutionizing urban living, a critical challenge has emerged: ensuring cybersecurity, data integrity, and trust management. A groundbreaking study published in the journal *Nature Scientific Reports* offers a promising solution—a Decentralized Trust Framework that harnesses the power of blockchain technology, AI-driven threat detection, and a novel consensus mechanism to fortify smart city infrastructures.
Led by Rafiqul Islam, a researcher at the Computer Science and Engineering department of Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, part of the JIS Group, the study introduces a multi-layered framework designed to address the vulnerabilities inherent in smart city systems. “The rapid evolution of smart cities has brought transformative advancements, but it has also exposed critical gaps in cybersecurity and data integrity,” Islam explains. “Our framework aims to bridge these gaps by providing a secure, scalable, and efficient solution.”
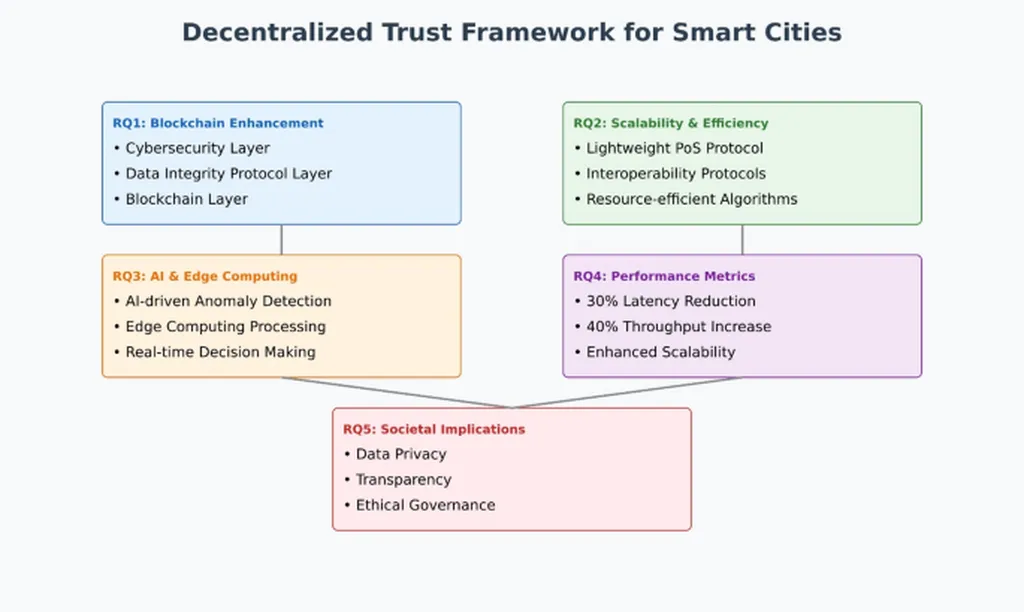
The framework comprises three key layers: a Blockchain Layer for decentralized trust and immutability, a Cybersecurity Layer employing cryptographic standards and AI-based anomaly detection, and a Data Integrity Protocol Layer for real-time synchronization and tamper-proof data validation. This innovative approach not only enhances security but also optimizes resource usage, nearly doubling the battery life of IoT devices.
For the energy sector, the implications are significant. Smart grids, energy management systems, and public safety networks stand to benefit from the framework’s ability to ensure data integrity and secure transactions. “The energy sector is increasingly reliant on data-driven systems for efficient operation and management,” Islam notes. “Our framework provides a robust foundation for building sustainable and resilient urban ecosystems, ensuring that these systems are secure and trustworthy.”
Performance evaluations of the framework have shown impressive results, including a threefold increase in transaction throughput, a 30% reduction in latency, and enhanced energy efficiency compared to traditional blockchain systems. Security metrics highlight a 98.2% threat detection rate and a substantial reduction in false positives, making it a compelling solution for critical smart city applications.
However, the journey towards widespread adoption is not without challenges. Issues such as interoperability among heterogeneous systems, computational overhead for IoT devices, and policy adoption remain. “While our framework offers significant advancements, there are still hurdles to overcome,” Islam acknowledges. “Future research will focus on optimizing interoperability protocols, incorporating quantum-resistant cryptographic techniques, and extending the framework to emerging domains such as autonomous systems and smart healthcare.”
The study, published in *Nature Scientific Reports*, represents a significant step forward in the quest to build sustainable, resilient, and trustworthy urban ecosystems. By addressing the critical vulnerabilities in smart city technologies, the Decentralized Trust Framework paves the way for a future where urban infrastructures are not only smart but also secure and efficient.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the integration of such advanced technologies will be crucial in ensuring the reliability and security of smart grids and energy management systems. The research by Rafiqul Islam and his team offers a glimpse into a future where data integrity and cybersecurity are paramount, shaping the development of smart cities and the energy sector for years to come.