In the heart of Cairo, Egypt, Hilmy Awad, an associate professor at Helwan University’s Department of Electrical Technology, is spearheading a revolution in renewable energy integration. His latest research, published in the journal Technologies, delves into the transformative potential of next-generation smart inverters, devices that could redefine how we harness and distribute clean energy.
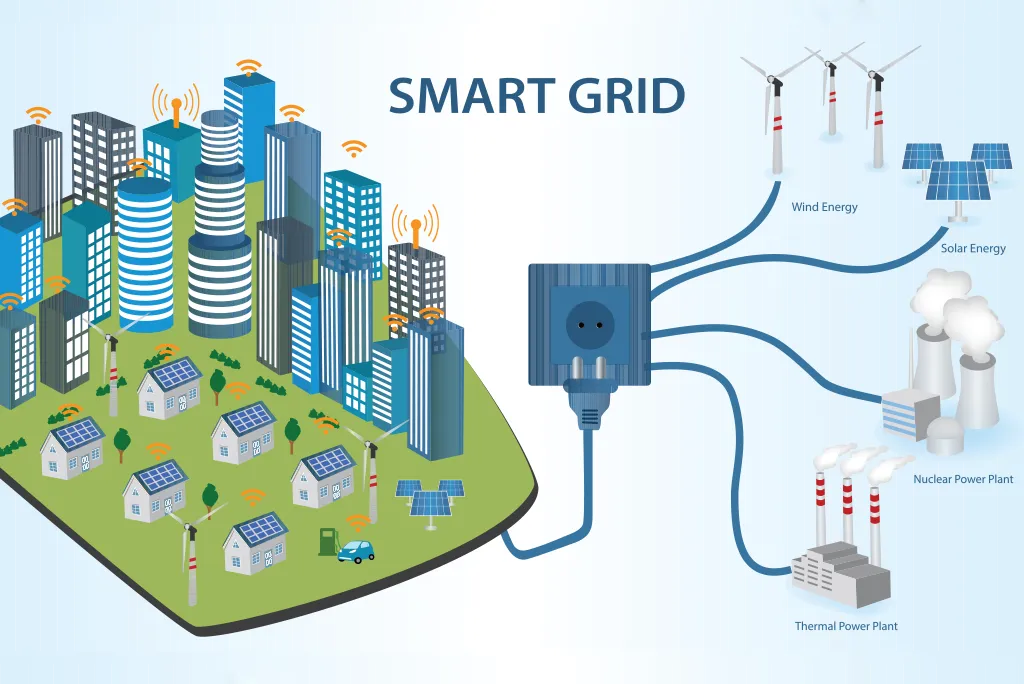
As the world races to decarbonize, renewable energy sources like solar and wind have become indispensable. However, their intermittent nature and distributed integration pose significant challenges to grid stability and power quality. Enter smart inverters, advanced devices that actively manage their interaction with the power grid, ensuring stability and efficiency.
“Smart inverters are not just about converting DC to AC,” Awad explains. “They constantly monitor the grid’s voltage and frequency, making real-time adjustments to maintain stability. They can inject or absorb reactive power, help regulate voltage levels, and even prevent blackouts during grid disturbances.”
The global smart inverter market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of over 15% from 2023 to 2030, driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and the need for grid stability. However, despite their potential, smart inverters face several hurdles, including interoperability issues, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and regulatory misalignments.
Awad’s research, which reviews advancements from 2018 to 2025, identifies these challenges and proposes actionable pathways for future innovation. He emphasizes the need for harmonized standards and supportive policy frameworks to facilitate the deployment of AI-enabled smart inverters.
One of the most promising developments in smart inverter technology is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI-driven grid-forming inverters can enhance grid stability and resilience by predicting and responding to grid disturbances in real-time. However, their widespread adoption is hindered by the absence of unified standards and misaligned policy frameworks.
The commercial implications of this research are vast. For energy companies, investing in smart inverter technology could lead to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. For policymakers, supporting the development and deployment of smart inverters could accelerate the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Awad’s work serves as a foundational reference for researchers and policymakers aiming to address technical and systemic bottlenecks in smart inverter deployment. By bridging theoretical advancements and real-world applicability, his research charts a roadmap for overcoming existing barriers and advancing smart inverter technology.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the role of smart inverters will become increasingly crucial. Awad’s research provides a comprehensive review of smart inverter technologies, emphasizing their role in renewable energy applications, advanced control strategies, and unresolved challenges. It is a call to action for the energy sector to embrace this transformative technology and pave the way for a sustainable energy future.