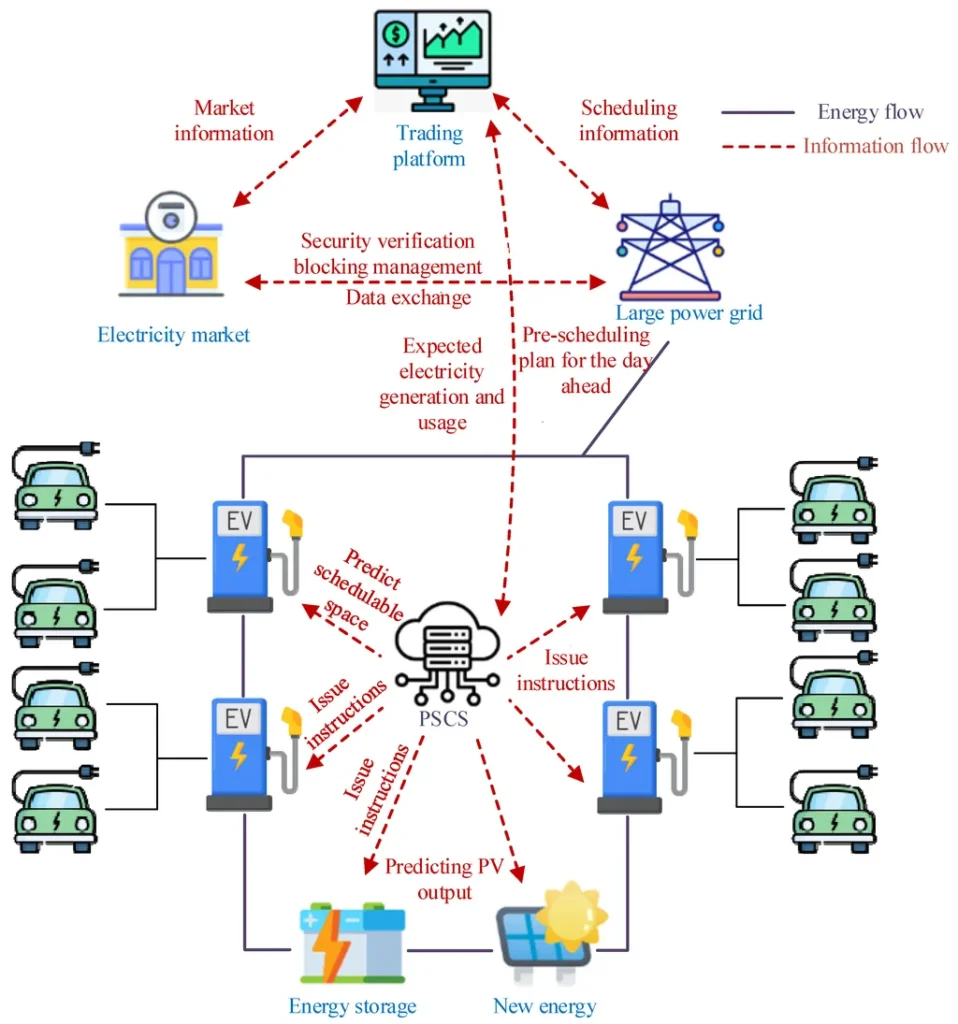
In a significant advancement for the energy sector, researchers have unveiled a novel two-stage bidding strategy for photovoltaic storage charging stations (PSCSs) that could reshape how electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sources interact in the electricity market. This groundbreaking study, led by Fulu Yan from the Linfen Power Supply Company, offers a comprehensive approach to optimizing the operational efficiency of PSCSs, which are poised to play a vital role in achieving the ambitious “dual-carbon” strategy aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
The research addresses a pressing challenge in the energy landscape: the inherent volatility of renewable energy generation and the unpredictable nature of EV charging demands. “As we integrate more renewable sources into our power systems, we must also enhance our strategies for managing these resources effectively,” Yan stated. The two-stage bidding model developed in this study not only aims to reduce costs but also enhances the market power of PSCSs, allowing them to flexibly dispatch resources and maximize revenue.
At its core, the new bidding strategy is designed to optimize the power purchase process for PSCSs. Stage I focuses on minimizing the costs associated with power bought by a PSCS, while Stage II seeks to lower the grid operator’s purchase costs, thereby optimizing the overall power balance within the system. This dual approach addresses the complexities of energy management in a market increasingly dominated by renewable sources and EVs.
One of the standout features of this research is its incorporation of a bidding space model that captures the competitive and cooperative dynamics among multiple charging stations. This aspect is particularly crucial as the electricity market evolves, with multiple charging station operators vying for market share. “Our model allows PSCSs to not only compete but also collaborate, which is essential for maximizing efficiency and profitability,” Yan explained.
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical models. By employing mixed-integer linear programming and advanced computational techniques, the study demonstrates that PSCSs can achieve substantial reductions in day-ahead power purchase costs. This translates directly into financial benefits for operators, potentially leading to lower charging costs for consumers as well. Moreover, the ability to adapt to market conditions and respond to fluctuations in demand positions PSCSs as agile players in a competitive environment.
As the energy sector continues to embrace renewable resources and electric mobility, the findings from this study published in the World Electric Vehicle Journal (translated from Chinese as “World Electric Vehicle Journal”) could serve as a catalyst for future developments. The proposed strategies not only promise enhanced operational efficiency but also pave the way for more integrated energy systems that leverage distributed energy resources effectively.
Looking ahead, Yan and his team are poised to explore additional innovations, including blockchain technology to secure transactions and safeguard system operations. The potential for regulatory impacts on multi-PSCS bidding strategies also remains an area of interest, as policymakers increasingly recognize the importance of integrating renewable energy and electric mobility into the grid.
In a world where energy management is becoming ever more complex, this research stands out as a beacon of innovation, offering practical solutions that could significantly influence the future of energy markets. The integration of advanced bidding strategies may well define the next generation of energy management, ensuring that as we move towards a greener future, we do so with efficiency and foresight.