Researchers from the University of Texas at Austin, including Simon Montoya-Bedoya, Tyler M. McGee, Joong Seok Lee, Sasha Litvinov, Ofodike A. Ezekoye, Donal P. Finegan, and Michael R. Haberman, have conducted a comprehensive review of ultrasonic testing (UT) methods for monitoring, damage detection, and processing of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) throughout their life-cycle. Their work, published in the Journal of Power Sources, aims to bridge the gap in understanding the behavior of LIBs, which are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and grid-level energy storage applications.
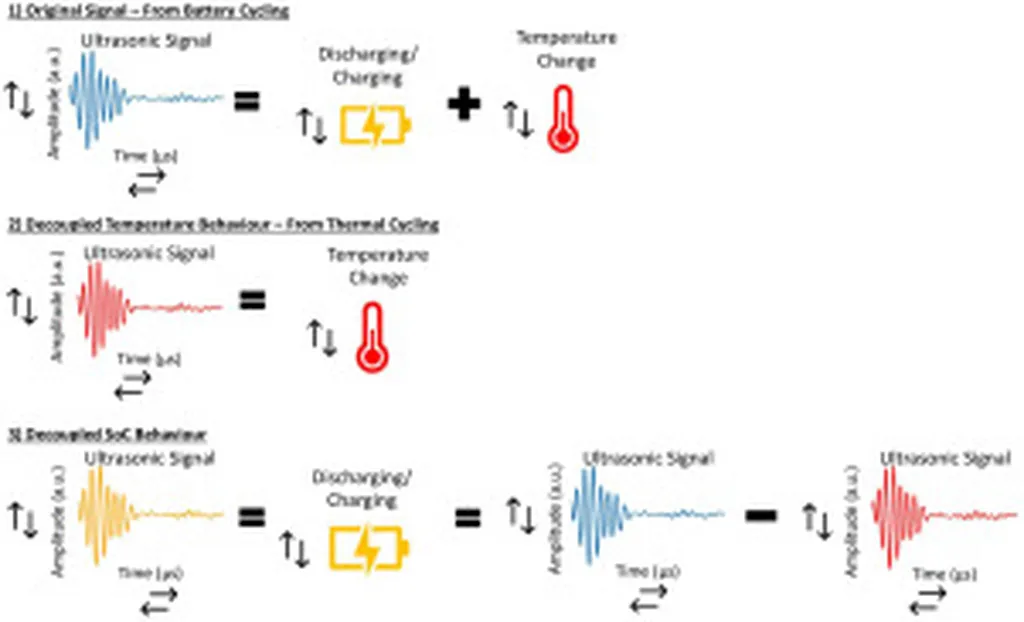
Currently, monitoring systems for LIBs rely primarily on electrical and temperature measurements, which provide limited information about the complex electrochemical processes occurring within the batteries. Ultrasonic testing has emerged as a promising non-invasive alternative due to its ease of use and sensitivity to mechanical changes that correlate with electrochemical changes. The researchers summarize the existing research on UT methods applied to LIBs at various stages of their life-cycle, highlighting relevant techniques for each stage.
The review also discusses physics-based and data-driven modeling approaches used to interpret ultrasonic signals in the context of LIBs. A significant challenge identified is establishing rigorous links between electrochemical behavior and elastic and poroelastic wave physics. Overcoming this challenge could provide deeper insights into the physical changes in LIBs that can be directly measured using UT.
Implementing UT across the LIB life-cycle presents several challenges, but the researchers also identify opportunities for further research. By addressing these challenges and exploring new avenues, UT could become a valuable tool for enhancing the safety, performance, and longevity of LIBs. This review serves as a helpful guide for researchers and practitioners in the growing field of UT for electrochemical battery systems, offering practical applications for the energy sector.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.