In the realm of energy journalism, it’s crucial to shed light on innovative research that can drive the sector towards a more sustainable future. Today, we turn our attention to a study that explores the intersection of blockchain technology and renewable energy certificates, with potential implications for the energy industry.
The research was conducted by Wei-Jen Liu, Wei-Yu Chiu, and Weiqi Hua, who are affiliated with the Department of Electrical Engineering at National Taiwan University. Their work, titled “Blockchain-Enabled Renewable Energy Certificate Trading: A Secure and Privacy-Preserving Approach,” was recently published in the IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, a reputable journal in the field of industrial and systems engineering.
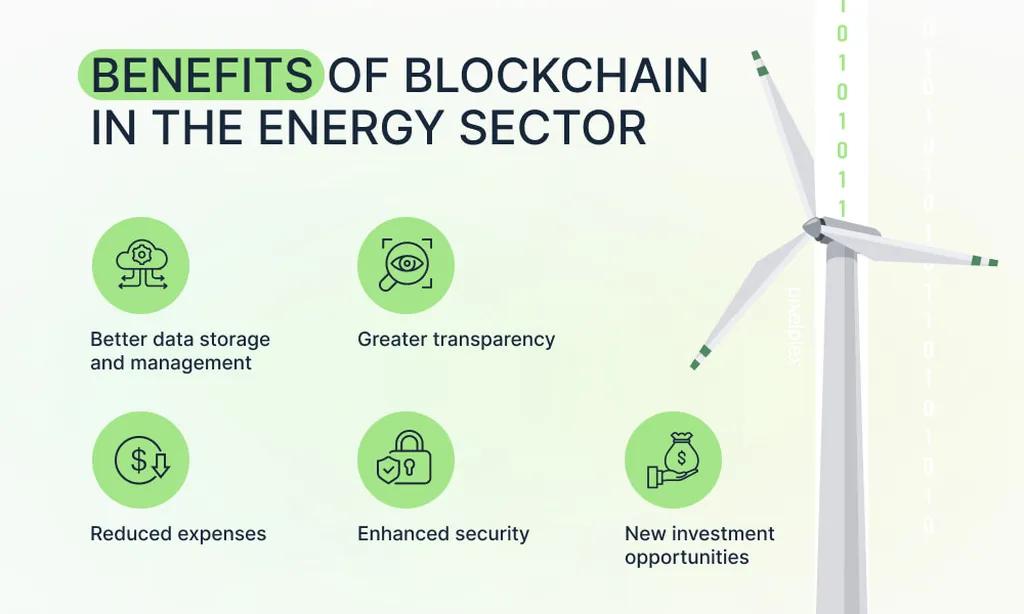
The study addresses two significant challenges in the current Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) system. Firstly, the lack of global adoption due to inconsistent design, and secondly, the inadequate incorporation of consumer privacy in blockchain designs. To tackle these issues, the researchers propose a new trading schema using a directed acyclic graph (DAG) blockchain system. This approach aims to protect consumer information while facilitating the trading of RECs between suppliers and consumers.
The findings of the study are promising. The proposed schema demonstrates a 41% reduction in transaction time and a 65% decrease in energy consumption compared to the proof-of-stake method. These improvements could make the REC system more efficient and environmentally friendly, aligning with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
In practical terms, this research could have several applications for the energy sector. For instance, it could help energy companies streamline their REC trading processes, reducing costs and improving transparency. Moreover, the enhanced privacy features could encourage more consumers to participate in the REC market, further driving the demand for renewable energy.
The study also highlights the potential of blockchain technology in the energy sector. By providing a secure and efficient platform for REC trading, blockchain could play a crucial role in the transition to renewable energy sources. This could contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and help meet the growing demand for clean energy.
In conclusion, the research conducted by Liu, Chiu, and Hua offers a promising approach to improving the REC system. By leveraging blockchain technology, the proposed schema could enhance the efficiency, privacy, and environmental sustainability of REC trading. As the energy sector continues to evolve, such innovations will be instrumental in driving the transition to a low-carbon future.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.