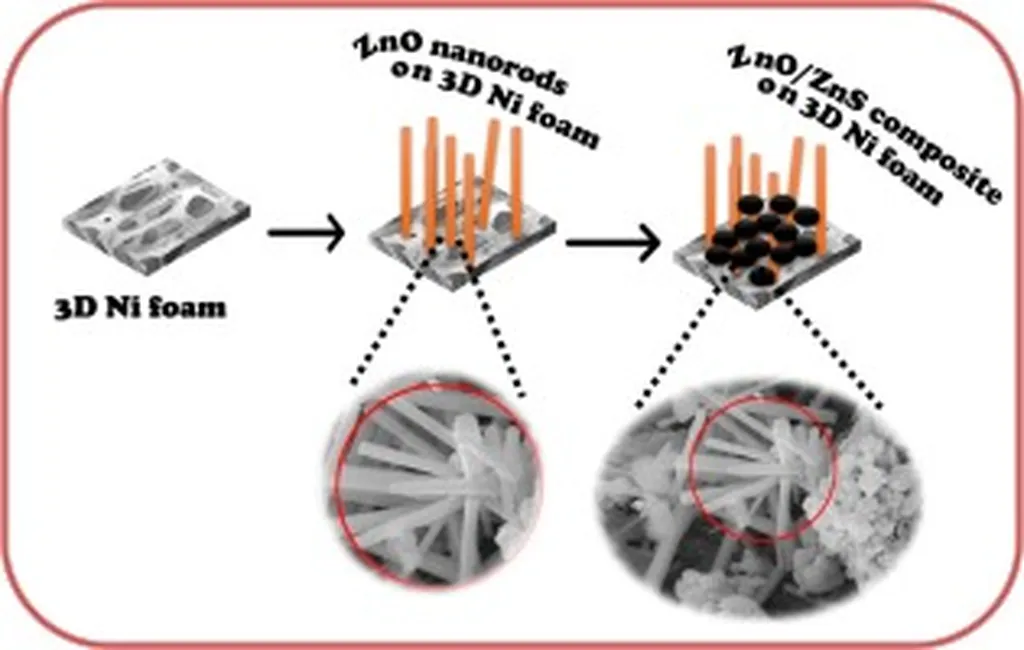
In the quest for sustainable and affordable energy solutions, a team of researchers from various institutions, including the University of Catania, the Italian Institute of Technology, and the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, has been exploring the potential of nanomaterials to enhance electrochemical energy storage systems.
The study, published in the journal Nanoscale, focuses on the use of zinc oxide/zinc sulfide (ZnO/ZnS) nanostructures to improve the performance of nickel foam (NF) in energy storage applications. The researchers employed hydrothermal growth methods to decorate the nickel foam with these nanostructures and then evaluated the morphology, structure, and composition using advanced electron microscopy techniques.
The electrochemical performance of the ZnO/ZnS-decorated nickel foam was assessed through cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements. The results indicated a predominant pseudocapacitive behavior when nickel foam was used as the substrate. This behavior is characterized by fast charge/discharge processes and high energy storage capacity, making it highly suitable for energy storage applications. In contrast, graphene paper (GP) exhibited a more modest and primarily capacitive performance, which is less efficient for energy storage.
To further understand the underlying mechanisms, the researchers conducted Mott-Schottky (M-S) and open circuit potential (OCP) measurements. These analyses suggested that the presence of a hole reservoir in the ZnS decoration plays a crucial role in enhancing the performance of the nickel foam. The hole reservoir facilitates the movement of charge carriers, thereby improving the overall energy storage efficiency.
The practical applications of this research for the energy sector are significant. The development of low-cost and environmentally friendly electrochemical energy storage systems is essential for addressing the growing global energy demand. By leveraging the unique properties of ZnO/ZnS nanostructures, the researchers have demonstrated a promising approach to enhancing the performance of nickel foam-based energy storage devices. This could lead to more efficient and sustainable energy storage solutions, contributing to the broader adoption of renewable energy sources.
In summary, the study highlights the potential of nanomaterials to revolutionize electrochemical energy storage systems. The findings provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the enhanced performance of ZnO/ZnS-decorated nickel foam, paving the way for further advancements in the field of energy storage.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.