In the realm of energy research, a team of scientists from Nanyang Technological University in Singapore has developed a new method to aid in the evaluation of renewable energy technologies. The researchers, Ding Ding, Yang Li, Poh Ling Neo, Zhiyuan Wang, and Chongwu Xia, have proposed a novel approach called the Subjective-Objective Median-based Importance Technique (SOMIT) to help decision-makers better understand the trade-offs involved in renewable energy projects. Their work was recently published in the journal Energy Policy.
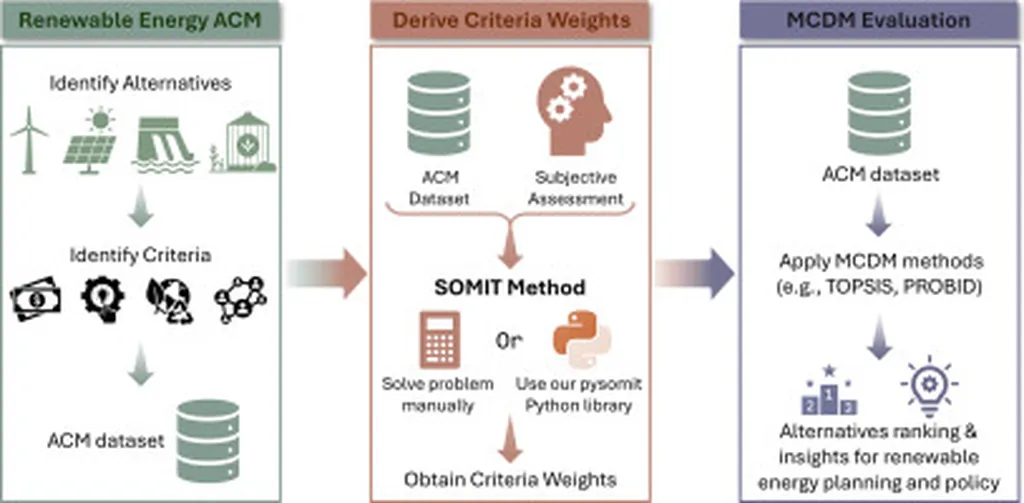
The transition to renewable energy is a complex process that involves considering various factors such as financial costs, technical feasibility, environmental impact, and social acceptance. Decision-makers often use a method called multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) to weigh these different factors and compare various renewable energy technologies. However, determining the appropriate weights for each factor can be challenging. Traditional methods rely either on subjective assessments from experts or objective data, both of which have their limitations.
The researchers developed SOMIT to address these challenges. This hybrid approach combines subjective expert knowledge with objective data to determine the weights of different criteria in the MCDM process. One of the key advantages of SOMIT is that it reduces the number of subjective comparisons needed, making the process less cognitively burdensome for experts. Additionally, SOMIT is more robust to outliers in the data, providing more reliable results.
The researchers demonstrated the practical utility of SOMIT through two case studies in India and Saudi Arabia. They used SOMIT to determine the weights of different criteria for evaluating renewable energy technologies in these countries. Then, they used the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) method to rank the renewable energy alternatives based on these weights. In both cases, solar power emerged as the top-performing renewable energy technology.
The researchers also developed a Python library called pysomit to make SOMIT more accessible to other researchers and practitioners. This library allows users to easily implement SOMIT in their own renewable energy evaluations.
In summary, SOMIT is a promising new method for evaluating renewable energy technologies. By combining subjective and objective approaches, it provides a more robust and reliable way to weigh different criteria in the MCDM process. This can help decision-makers make more informed choices about renewable energy projects, ultimately accelerating the transition to a more sustainable energy future. The research was published in the journal Energy Policy.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.