In the realm of academic publishing, the concept of diamond open access—where journals are free to both readers and authors—has long been championed, particularly within the field of mathematics. However, the implementation of this model has faced significant challenges, with relatively few journals adopting it. A recent article published in the journal “Diamond Open Access: The AMR Experiment” delves into the experiences of the Association for Mathematical Research (AMR) in establishing and maintaining diamond open access journals. The research is led by Alex Kontorovich, a mathematician affiliated with Rutgers University.
The study focuses on the infrastructure, costs, and editorial practices that make the diamond open access model viable. Kontorovich and his colleagues aim to shed light on why previous attempts at reform have been difficult to replicate and how a lightweight institutional framework can lower the barriers to adoption. By documenting the AMR’s journey, the researchers provide a practical roadmap for others interested in pursuing this model.
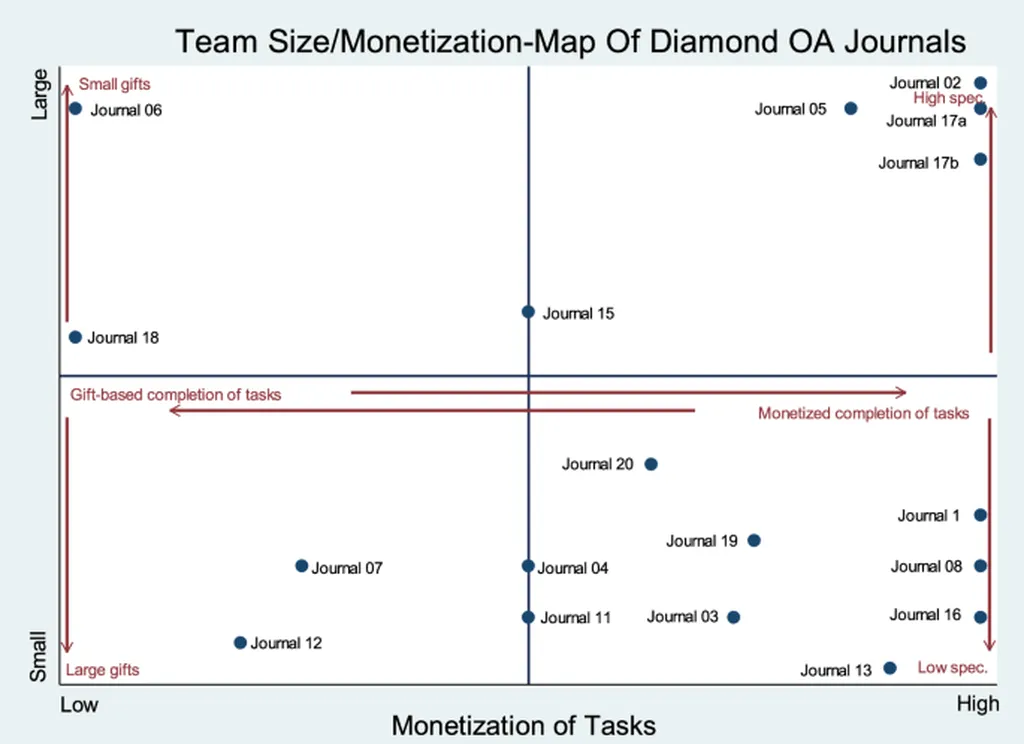
One of the key findings of the research is the importance of a robust infrastructure to support diamond open access journals. This includes the use of modern publishing platforms, efficient editorial workflows, and reliable systems for managing submissions and peer reviews. The study highlights the need for transparency in reporting costs and revenues, which can help build trust within the academic community and attract potential supporters.
The research also emphasizes the role of editorial practices in ensuring the quality and sustainability of diamond open access journals. This includes the implementation of rigorous peer review processes, the establishment of clear editorial guidelines, and the promotion of diversity and inclusion within the editorial board. By fostering a culture of excellence and collaboration, the AMR has been able to maintain high standards while keeping costs low.
In terms of practical applications for the energy sector, the findings of this research could be relevant for organizations looking to disseminate research findings more widely and democratize access to knowledge. For instance, energy research institutions could consider establishing diamond open access journals to share their work with a global audience, fostering collaboration and innovation. By adopting a lightweight institutional framework and leveraging modern publishing technologies, these institutions could lower the barriers to entry and make a significant contribution to the field.
In conclusion, the research led by Alex Kontorovich provides valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities of diamond open access publishing. By documenting the AMR’s experiences, the study offers a practical guide for others interested in pursuing this model, with potential applications extending beyond the realm of mathematics to the energy sector and other fields. The research was published in the journal “Diamond Open Access: The AMR Experiment,” contributing to the ongoing conversation about the future of academic publishing.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.