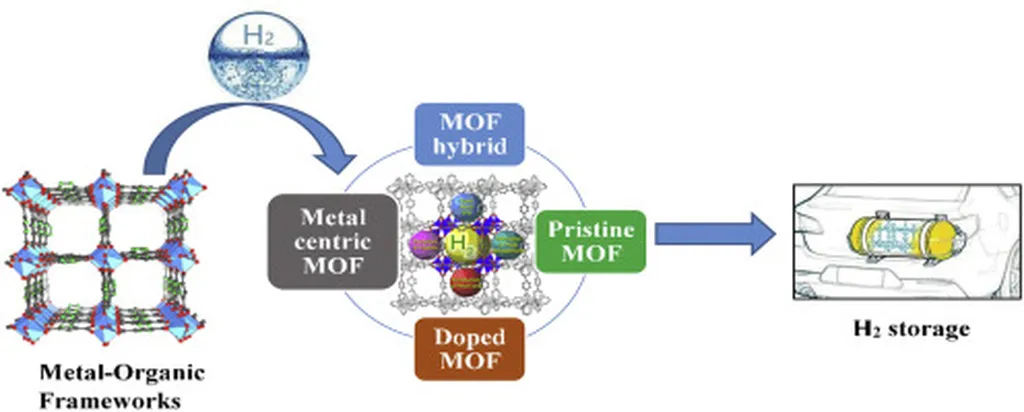
In the realm of energy storage and materials science, a trio of researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China, Yanhuai Ding, Dan Qian, and Zhipeng Liu, have been exploring the potential of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) to enhance hydrogen storage capabilities. Their recent study, published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A, focuses on Zr-based MOFs and the impact of metal ion substitution on their mechanical and hydrogen storage properties.
Metal-Organic Frameworks are a class of crystalline porous materials known for their versatility and wide range of applications, from gas storage to catalysis. Among these, Zr-based MOFs are notable for their stability and high surface area. The researchers investigated six key Zr-based MOFs: UIO-66, UIO-67, UIO-68, MOF-801, MOF-802, and MOF-841. Using advanced computational methods, including molecular dynamics, grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations, and density functional theory, they explored how substituting metal ions (Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) affects these MOFs.
The study revealed that metal ion substitution significantly influences the mechanical stability and hydrogen adsorption capacity of Zr-based MOFs. For instance, substituting Zr with other metal ions can enhance the mechanical properties of the MOFs, making them more robust and suitable for various industrial applications. Moreover, the hydrogen storage capacity of these MOFs can be fine-tuned by carefully selecting the dopant metal ion. This finding is crucial for the energy sector, particularly in the development of hydrogen storage solutions, which are essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy carrier.
The practical applications of this research are manifold. In the energy sector, improved hydrogen storage materials can facilitate the transition to a hydrogen economy, enabling more efficient and cost-effective storage and transportation of hydrogen fuel. Additionally, the enhanced mechanical properties of these MOFs can make them more durable and long-lasting, reducing maintenance costs and improving overall performance. The insights gained from this study provide a valuable roadmap for the design and optimization of high-performance MOF materials, paving the way for innovative solutions in energy storage and beyond.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.