Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China, led by Jun Li, have made significant strides in the field of quantum metrology, a technique that uses quantum mechanics to make highly precise measurements. Their work focuses on a phenomenon known as quantum Zeno dynamics (QZD), which can protect quantum information from noise and interference. This research could have profound implications for the energy sector, particularly in improving the precision of sensors and measurement devices used in energy production and distribution.
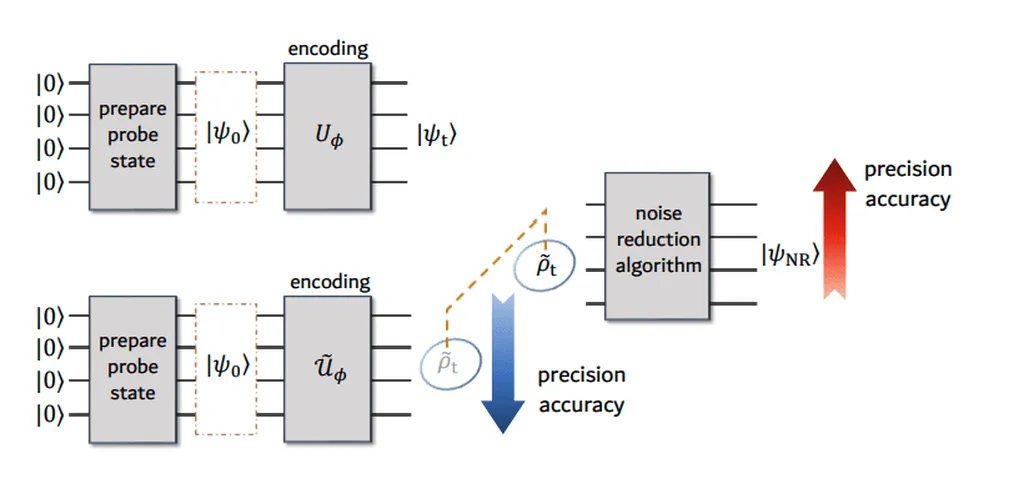
Quantum Zeno dynamics works by frequently measuring a quantum system, effectively freezing its evolution and protecting it from external noise. However, previous studies have faced challenges in applying QZD to practical metrology because the measurement process can interfere with the encoding of information. The researchers addressed this issue by introducing strong inter-particle interactions during the parameter encoding stage, allowing them to harness QZD for robust quantum metrology.
The team experimentally validated their approach using a nuclear magnetic resonance platform, achieving near-optimal precision scaling under amplitude damping in both parallel and sequential settings. This means that their method can significantly improve the accuracy of measurements even in the presence of noise. Numerical simulations further demonstrated the scalability of the approach and its compatibility with other control techniques for suppressing more general types of noise.
For the energy industry, this research could lead to the development of more precise and reliable sensors for monitoring energy systems. For example, in the oil and gas sector, accurate measurement of reservoir properties is crucial for efficient extraction and production. Similarly, in renewable energy, precise monitoring of wind speeds and solar radiation can improve the efficiency of energy generation. The application of QZD in quantum metrology could enhance the performance of these sensors, leading to more efficient and sustainable energy production.
The research was published in the journal Nature Communications, a highly respected peer-reviewed journal that covers all areas of the natural sciences. The findings highlight QZD as a powerful strategy for noise-resilient quantum metrology, paving the way for more advanced and accurate measurement techniques in various industries, including energy.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.