In the realm of autonomous vehicles and intelligent transportation systems, the ability to accurately detect objects in three dimensions is paramount for safety and reliability. Researchers from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Xiangxuan Ren and Zhongdao Wang, have developed a novel approach to 3D object detection that enhances the robustness and deployment flexibility of these systems.
The team’s work, titled “LiteFusion: Taming 3D Object Detectors from Vision-Based to Multi-Modal with Minimal Adaptation,” addresses the challenges posed by current multi-modal 3D object detectors. These detectors often rely heavily on LiDAR sensors and complex architectures, which can lead to significant performance drops when LiDAR is not available. Additionally, the reliance on 3D sparse convolution operators, which are optimized for NVIDIA GPUs, can make deployment on diverse hardware platforms difficult.
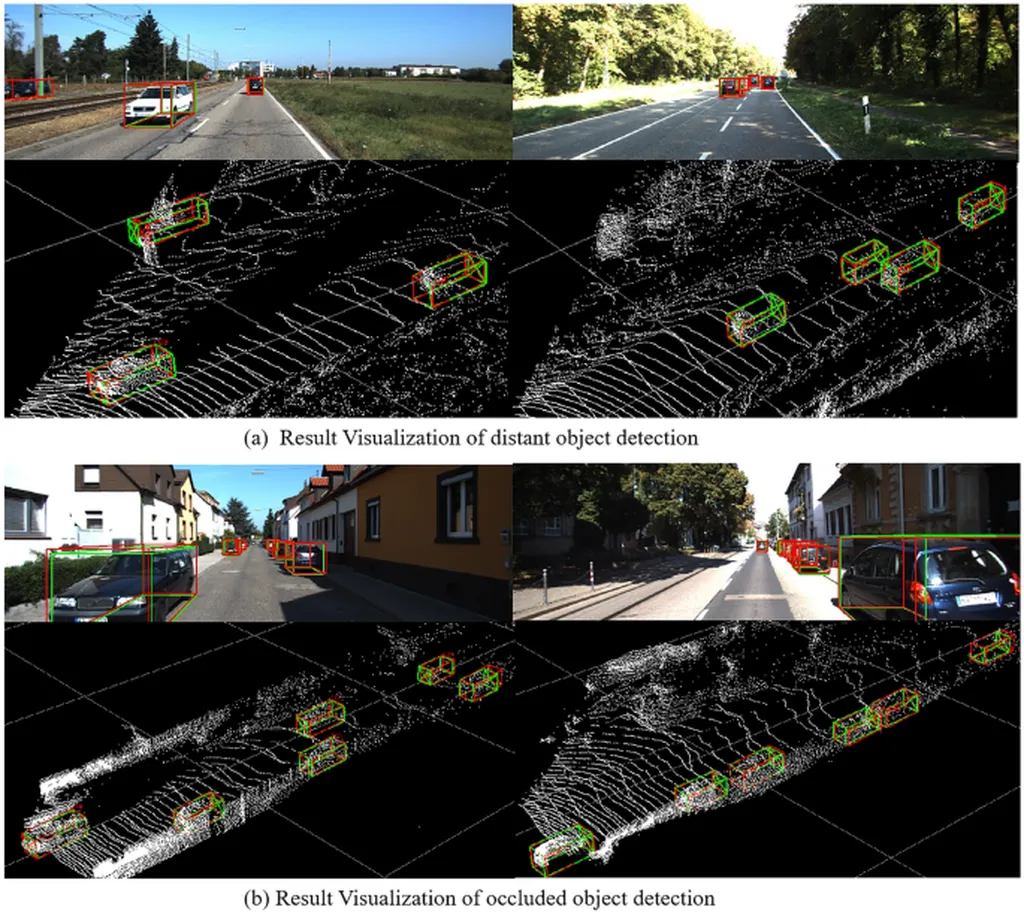
LiteFusion, the novel multi-modal 3D detector developed by the researchers, takes a different approach. Instead of treating LiDAR point clouds as an independent modality with a separate feature extraction backbone, LiteFusion uses LiDAR data as a complementary source of geometric information to enhance camera-based detection. This approach eliminates the need for a 3D backbone, making the method highly deployment-friendly.
The researchers integrated complementary features from LiDAR points into image features within a quaternion space, where orthogonal constraints are well-preserved during network training. This helps the model understand domain-specific relations across modalities, resulting in a compact cross-modal embedding. Experiments on the nuScenes dataset showed that LiteFusion improved the baseline vision-based detector by 20.4% mAP and 19.7% NDS with only a minimal increase in parameters (1.1%) and without using dedicated LiDAR encoders. Notably, LiteFusion maintained strong performance even in the absence of LiDAR input, highlighting its robustness and effectiveness across diverse fusion paradigms and deployment scenarios.
The research was published in the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), a premier international conference in the field of computer vision. The practical applications of this research for the energy sector could include enhancing the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles used in energy infrastructure monitoring, maintenance, and transportation. The deployment-friendly nature of LiteFusion could also make it easier to integrate advanced detection capabilities into existing energy sector systems, improving overall efficiency and safety.
In summary, LiteFusion represents a significant advancement in the field of 3D object detection, offering a more robust, flexible, and deployment-friendly solution for intelligent transportation systems and other applications that require high-accuracy object detection.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.