Researchers from the Department of Materials Science and Nanotechnology Engineering at Abdullah Gül University in Turkey have made significant strides in optimizing the growth conditions for ultrathin hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) films directly on dielectric substrates. Their work, published in the journal Applied Surface Science, focuses on leveraging the unique properties of h-BN for advanced optoelectronic applications in the energy sector.
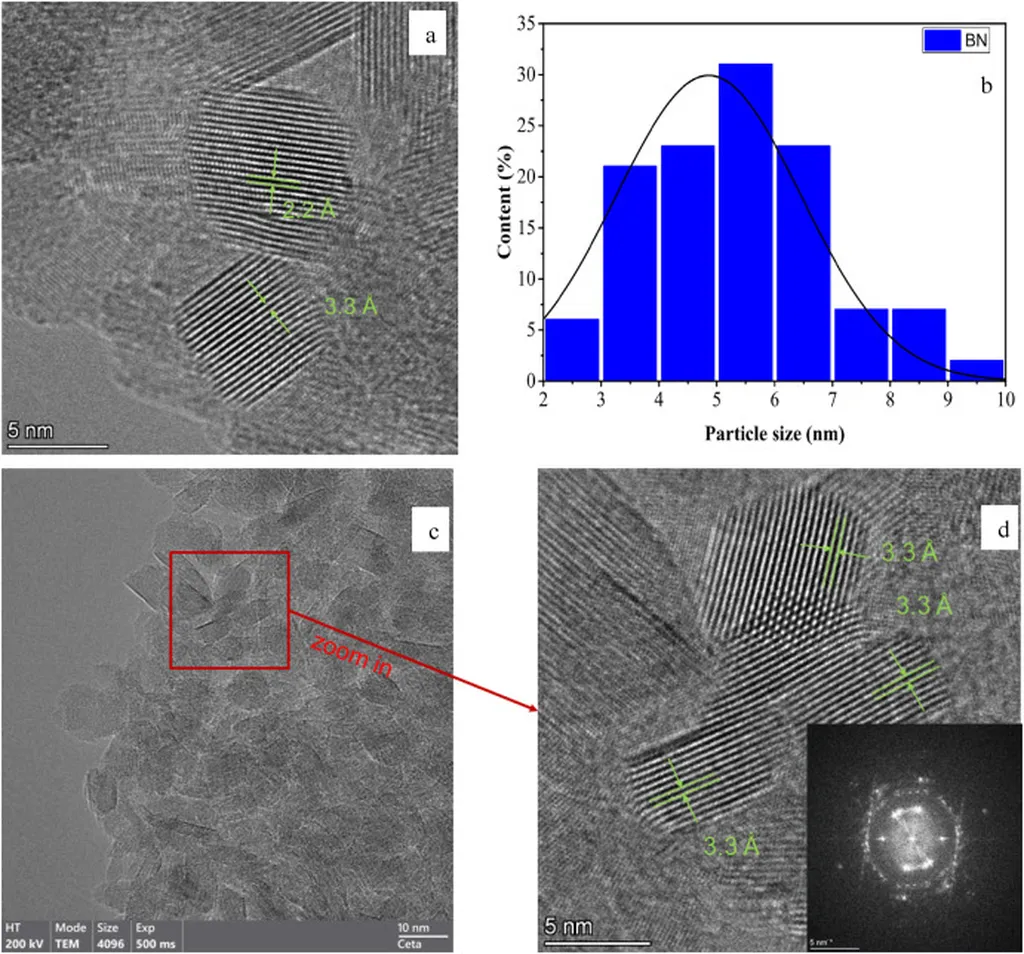
Hexagonal boron nitride is a material of great interest for applications such as deep ultraviolet (DUV) photodetectors, UV sensing and communication systems, and solar cells. Its attractive properties include a wide, layer-dependent energy bandgap, superior mechanical strength, high thermal conductivity, and exceptional transparency in the UV region. Traditionally, h-BN thin films are synthesized using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods on catalytic substrates like copper and nickel. However, transferring the synthesized h-BN to target substrates for device integration often results in material damage, such as folding, cracking, and polymer residues, which degrade the material’s optoelectronic properties.
To address this challenge, the researchers aimed to synthesize high-quality h-BN films directly on dielectric substrates, such as silicon, SiO2, quartz, sapphire, or AlN, eliminating the need for transfer. The primary difficulty in direct synthesis is achieving homogeneous, high-crystallinity films with controllable thickness due to the absence of a catalytic effect. The team investigated the optimization of growth parameters for direct synthesis of ultrathin h-BN films on non-catalytic quartz substrates using the low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) method.
The optimal synthesis conditions were determined to be 1050°C for 60 minutes, achieved by the decomposition of 150 mg of ammonia borane (AB) precursor at 80°C. This optimization is crucial for advancing large-scale, high-performance h-BN-based DUV photodetector fabrication. The ability to synthesize h-BN directly on dielectric substrates without the need for transfer processes can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of optoelectronic devices in the energy sector, particularly in applications requiring UV detection and communication.
The researchers’ work represents a significant step forward in the development of advanced materials for energy applications, offering practical solutions to longstanding challenges in the synthesis and integration of h-BN films. As the energy sector continues to explore innovative materials and technologies, the insights gained from this research could pave the way for more efficient and reliable optoelectronic devices.
Source: Bozkaya, M., Arık, M.N., Altuntepe, A., Ateş, H., & Zan, R. (2023). Optimization for growth condition of ultrathin hexagonal boron nitride on dielectric substrates via LPCVD. Applied Surface Science, 159894.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.