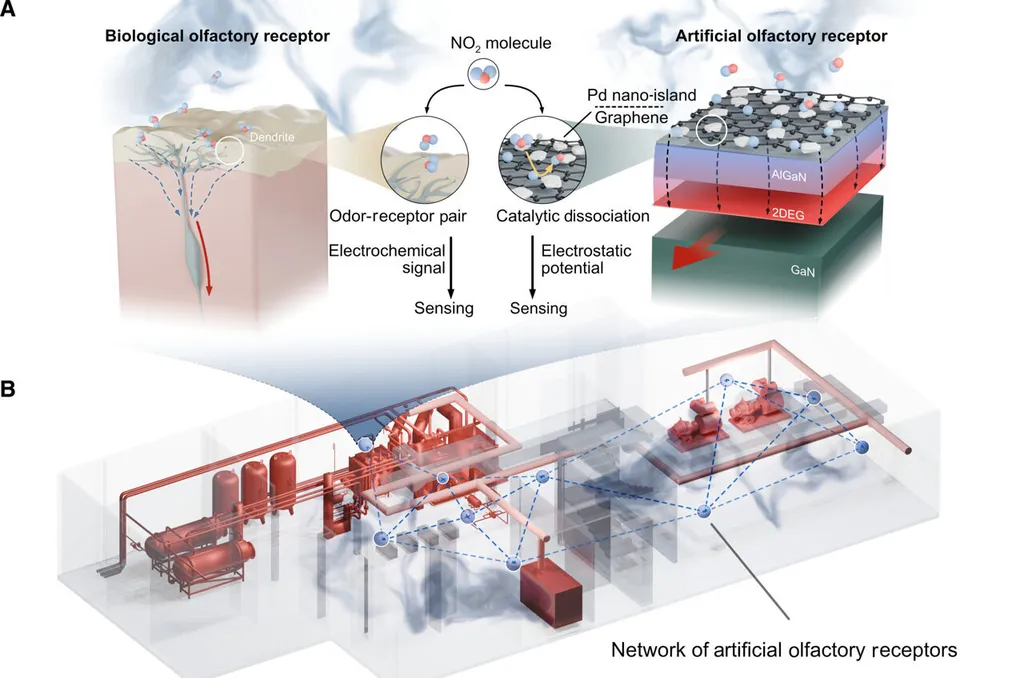
Researchers from the University of Oklahoma, led by Zifan Zhou and Bin Li, have developed a novel digital twin framework called AIMNET for continuous monitoring and early detection of gas emissions. This technology integrates IoT-based sensing networks with advanced weather-gas transport models to provide real-time, high-resolution data on carbon-based gas plumes. The research was published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
AIMNET is designed to enhance environmental hazard management by enabling timely and effective mitigation responses to industrial gas leaks and wildfire outbreaks. The framework consists of three layers: a physical world with custom-built monitoring devices, bidirectional information feedback links for intelligent data transmission and control, and a digital twin world that uses AI-driven analytics for prediction, anomaly detection, and dynamic modeling of weather-gas interactions.
The researchers deployed a small-scale distributed sensing network over an oil and gas production basin to demonstrate AIMNET’s scalability and energy efficiency in remote environments. Additionally, a mobile-based emission monitoring network was set up around a wastewater treatment plant to capture methane emission events. The preliminary results successfully detected and resolved the dynamics of these emissions through tiered model simulations.
AIMNET’s ability to provide real-time, high-resolution data on gas emissions offers significant practical applications for the energy sector. It can enhance safety and environmental compliance by enabling early detection of gas leaks, reducing the risk of accidents, and minimizing environmental impact. The framework’s predictive capabilities can also support better decision-making in emergency response and resource allocation.
Despite its promising results, the researchers acknowledge key implementation challenges, such as ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the sensing network and integrating the digital twin framework with existing industrial systems. They outline future directions for advancing AIMNET, including improving the resolution and coverage of the sensing network and enhancing the AI-driven analytics for more accurate predictions and anomaly detection.
In summary, AIMNET represents a significant advancement in digital twin technology for environmental monitoring. Its application in the energy sector can lead to improved safety, environmental compliance, and operational efficiency, making it a valuable tool for managing industrial hazards and mitigating their impact.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.