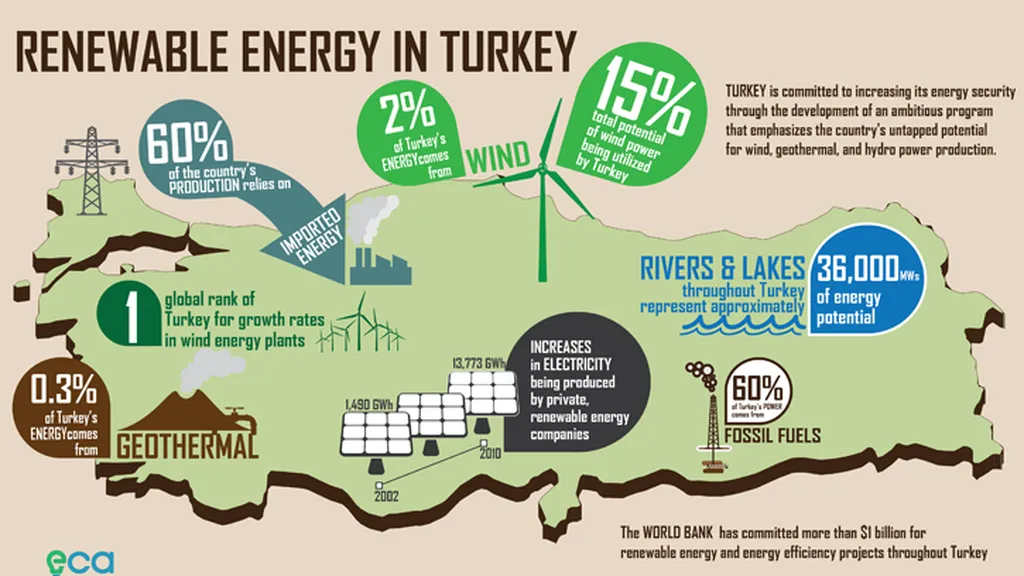
In the quest for sustainable development, Turkiye is exploring its options for renewable energy investments. A recent study by Emre Akusta and Raif Cergibozan from Istanbul Gelisim University aims to prioritize renewable energy sources to help achieve sustainable development goals in Turkiye. The research, published in the journal “Energy Policy,” uses a fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) method to evaluate and rank different renewable energy alternatives.
The study considers 30 criteria that influence investment decisions in renewable energy sources. These criteria are grouped into five main categories: economic, political, technical, environmental, and social. The researchers calculated the weights of these criteria to understand their importance in the decision-making process. They then analyzed which renewable energy sources are most advantageous according to each criterion.
The results indicate that economic criteria are the most important factor for renewable energy investments in Turkiye, followed by political, technical, environmental, and social criteria. Among the renewable energy sources, solar, wind, and hydroelectric power emerged as the most suitable options. Solar energy was found to be the most advantageous according to economic, political, and social criteria. Wind energy was prioritized for its technical feasibility, while hydroelectric power was also considered a strong contender.
This research provides valuable insights for policymakers and investors in Turkiye’s energy sector. By understanding the most influential criteria and the strengths of different renewable energy sources, stakeholders can make more informed decisions. The study highlights the importance of a multi-criteria approach in evaluating renewable energy investments, ensuring that economic, political, technical, environmental, and social factors are all considered. This holistic approach can help Turkiye achieve its sustainable development goals more effectively.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.