Researchers Hridya P and Mangilal Choudhary from the Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar, have conducted a study that delves into the intricacies of gas breakdown processes, specifically focusing on argon gas. Their work, published in the Journal of Applied Physics, sheds light on how electrode configurations and inter-electrode spacing influence the breakdown voltage of gases, a phenomenon governed by Paschen’s Law.
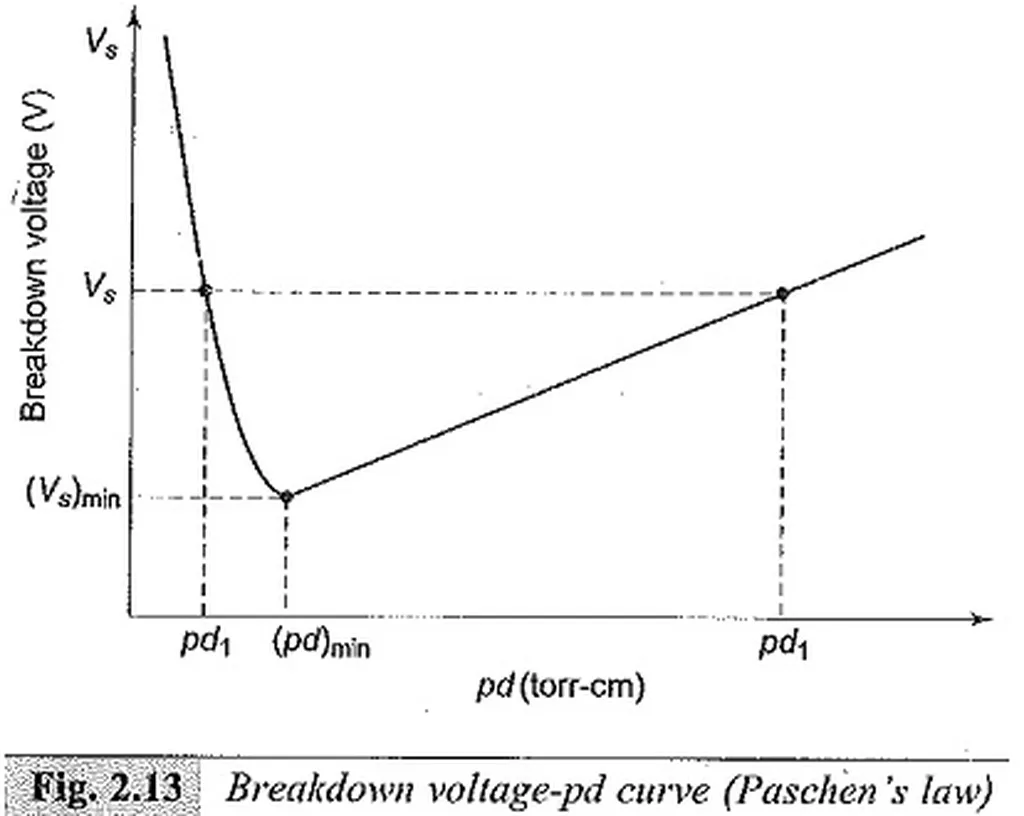
Paschen’s Law is a fundamental principle in gas discharge physics, which states that the breakdown voltage of a gas is a function of the product of gas pressure and inter-electrode distance (pd). This law predicts a characteristic minimum voltage at a specific pd value. However, the researchers noted that real-world applications often deviate from the ideal conditions assumed in Paschen’s Law. To better understand these deviations, they conducted numerous experiments using both symmetric and asymmetric electrode configurations of varying sizes.
The experiments yielded Paschen curves at different inter-electrode distances, which were then fitted using a modified empirical relation for breakdown voltage. This new relation incorporates variable power-law dependencies and fitting parameters, allowing it to more accurately capture the observed deviations from Paschen’s Law. The researchers found that the breakdown voltage and the corresponding pd value were indeed influenced by both the electrode configurations and the inter-electrode discharge gap.
To explain these variations, the researchers analyzed the electric field distributions between the electrodes (cathode and anode) for an applied voltage. Their findings have significant implications for the energy industry, particularly in the design and optimization of gas discharge devices such as gas-insulated switchgear, plasma processing tools, and lightning arresters. By understanding how electrode configurations and spacing affect gas breakdown, engineers can design more efficient and reliable devices.
In summary, the study by Hridya P and Mangilal Choudhary provides valuable insights into the complex interplay between electrode configurations, inter-electrode spacing, and gas breakdown processes. Their modified empirical relation offers a more accurate tool for predicting breakdown voltages in real-world applications, ultimately contributing to the advancement of gas discharge technologies in the energy sector. The research was published in the Journal of Applied Physics.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.