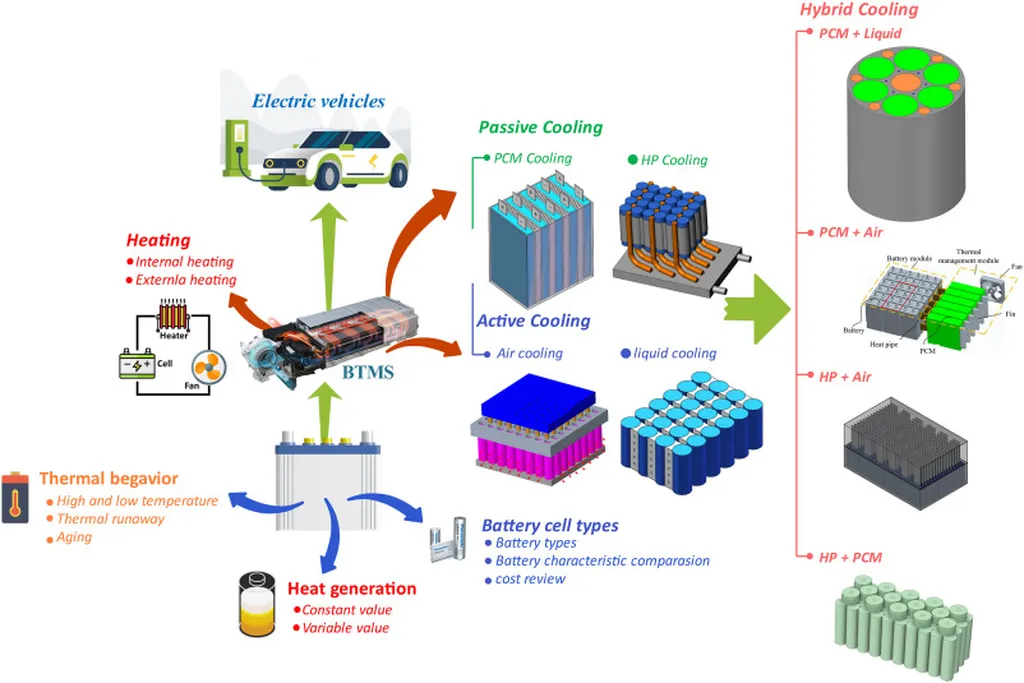
In the realm of energy journalism, a recent study conducted by researchers Reihaneh Jahedan, Satya Peddada, Mark Jennings, Sunil Katragadda, James Allison, and Nenad Miljkovic from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign has shed light on a critical aspect of battery electric vehicles (BEVs): thermal management systems (TMSs). This research, published in the journal Applied Energy, aims to streamline the design and optimization of TMSs, a crucial component for enhancing the performance and efficiency of BEVs.
As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, the design of effective TMSs for BEVs has become increasingly important. Unlike conventional vehicles, BEVs lack waste combustion heat and are highly sensitive to battery operating temperatures. Moreover, the energy consumption of TMSs significantly impacts the driving range of BEVs, making their design a complex task. While previous studies have focused on optimizing TMS configurations for varying ambient conditions, a comprehensive approach to exploring the potential of reconfigurable TMS architectures has been lacking.
The researchers addressed this gap by proposing a systematic method to automatically enumerate and simulate reconfigurable architectures for TMSs. Using graph modeling, they created a framework to conduct transient performance analysis and optimization-based trade-off studies among system performance, energy consumption, and complexity. The study explored over 150 operating mode sequences, narrowing down to 39 unique architectures for further evaluation.
MATLAB Simscape models of these architectures were automatically generated and their performance evaluated. The multi-objective optimization results provided decision support for selecting the best architecture based on user priorities. This approach not only simplifies the complex design landscape of multi-mode reconfigurable systems but also ensures that significant performance improvements are not overlooked.
The practical applications of this research for the energy sector are substantial. By optimizing TMSs, BEVs can achieve better battery performance and extended driving ranges, making them more competitive with conventional vehicles. Furthermore, the systematic method proposed by the researchers can be applied to other energy storage systems, enhancing their efficiency and reliability.
In conclusion, this study represents a significant step forward in the design and optimization of thermal management systems for battery electric vehicles. By providing a holistic approach to exploring reconfigurable TMS architectures, the researchers have opened new avenues for improving the performance and efficiency of BEVs, ultimately contributing to the advancement of the energy sector.
Source: Jahedan, R., Peddada, S., Jennings, M., Katragadda, S., Allison, J., & Miljkovic, N. (2023). Automated Enumeration of Reconfigurable Architectures for Thermal Management Systems in Battery Electric Vehicles. Applied Energy, 335, 120554.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.