The launch of the SUN-DT project marks a significant step forward in the evolution of concentrated solar power (CSP) technology, with implications that could reshape the renewable energy landscape. By uniting nine international organisations under the coordination of Spain’s National Renewable Energy Centre (CENER), this Horizon Europe-backed initiative aims to accelerate the digital transition of tower CSP systems, ensuring Europe maintains its leadership in next-generation renewable energy.
Joerg Widmer, principal investigator of the project and Research Director at IMDEA Networks, underscores the ambition: “SUN-DT pushes tower CSP technology into a fully digital era. By combining AI-based calibration, predictive maintenance and real-time optimisation, we enable plants to operate more efficiently and reliably than ever before. This project strengthens Europe’s technological leadership in renewable energy.”
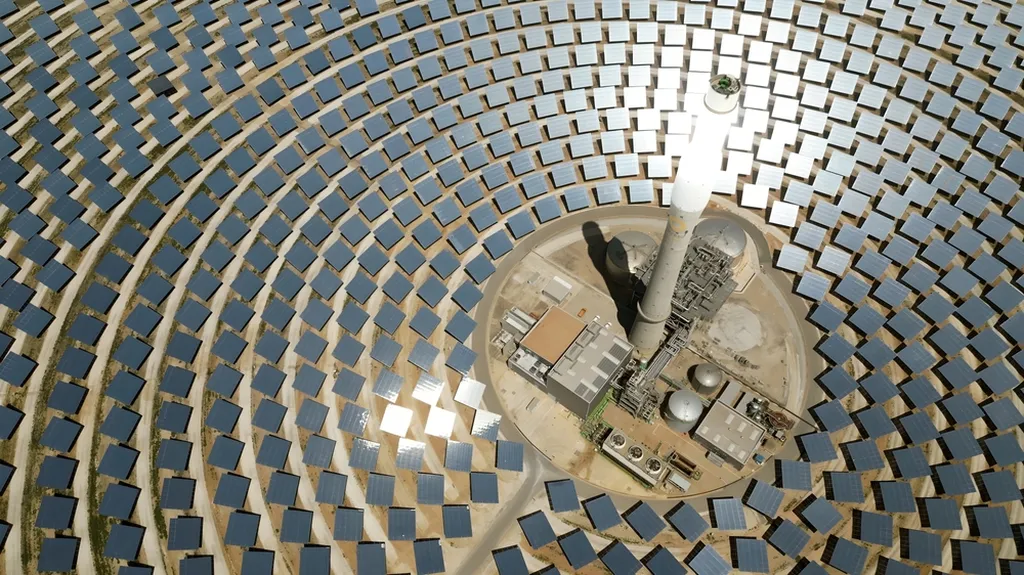
Tower CSP plants, which rely on vast fields of heliostats to concentrate sunlight onto a central receiver, have grown increasingly complex. Perfect synchronisation among thousands of heliostats, high-temperature receivers and thermal storage systems is critical, making digitalisation essential for improving efficiency, reducing optical losses and cutting costs. As global competition intensifies, SUN-DT seeks to close the digital gap, ensuring European-built CSP systems remain cutting-edge and cost-competitive.
IMDEA Networks, a central partner in the consortium, leads the development of a 5G communication layer that will support precise heliostat characterisation and calibration. This wireless infrastructure is vital for scaling the technology, enabling high-capacity data links, real-time monitoring and rapid feedback loops that allow operators to correct misalignment instantly. IMDEA’s expertise in wireless sensing, network architecture and experimental testbeds ensures that advanced control strategies can be deployed reliably in operating CSP plants.
At the heart of SUN-DT is a suite of interoperable digital tools designed to modernise every layer of tower CSP operations. The system includes automated heliostat calibration software, a digital twin for real-time decision-making, an energy-dispatch optimisation engine and predictive maintenance capabilities. These tools aim to improve solar-field performance, minimise downtime, lower operational and maintenance costs and enhance CSP’s role in grid-support services. The unified SUN-DT platform integrates data, analytics and optimisation methods into a single operational environment, increasing efficiency and reducing deployment costs for future projects.
To validate its results, SUN-DT will undergo rigorous testing at two experimental facilities and two major commercial tower CSP plants: Khi Solar One in South Africa and Cerro Dominador in Chile. These sites, operated by consortium partners COX and ACCIONA, represent different design configurations and provide ideal conditions for demonstrating performance gains in real-world environments. One of the project’s most promising outcomes is an automated calibration system capable of detecting heliostat misalignment as it happens, allowing operators to intervene only where needed, improving optical efficiency and reducing field maintenance time.
SUN-DT ultimately aims to usher tower CSP plants into a fully digital era, enhancing their reliability, cutting operating costs and making renewable solar thermal energy more competitive on a global scale. This initiative could set a new benchmark for CSP technology, influencing how renewable energy projects are designed, operated and maintained worldwide. As the sector evolves, the lessons learned from SUN-DT may well define the future of solar thermal power, reinforcing Europe’s position as a leader in sustainable energy innovation.