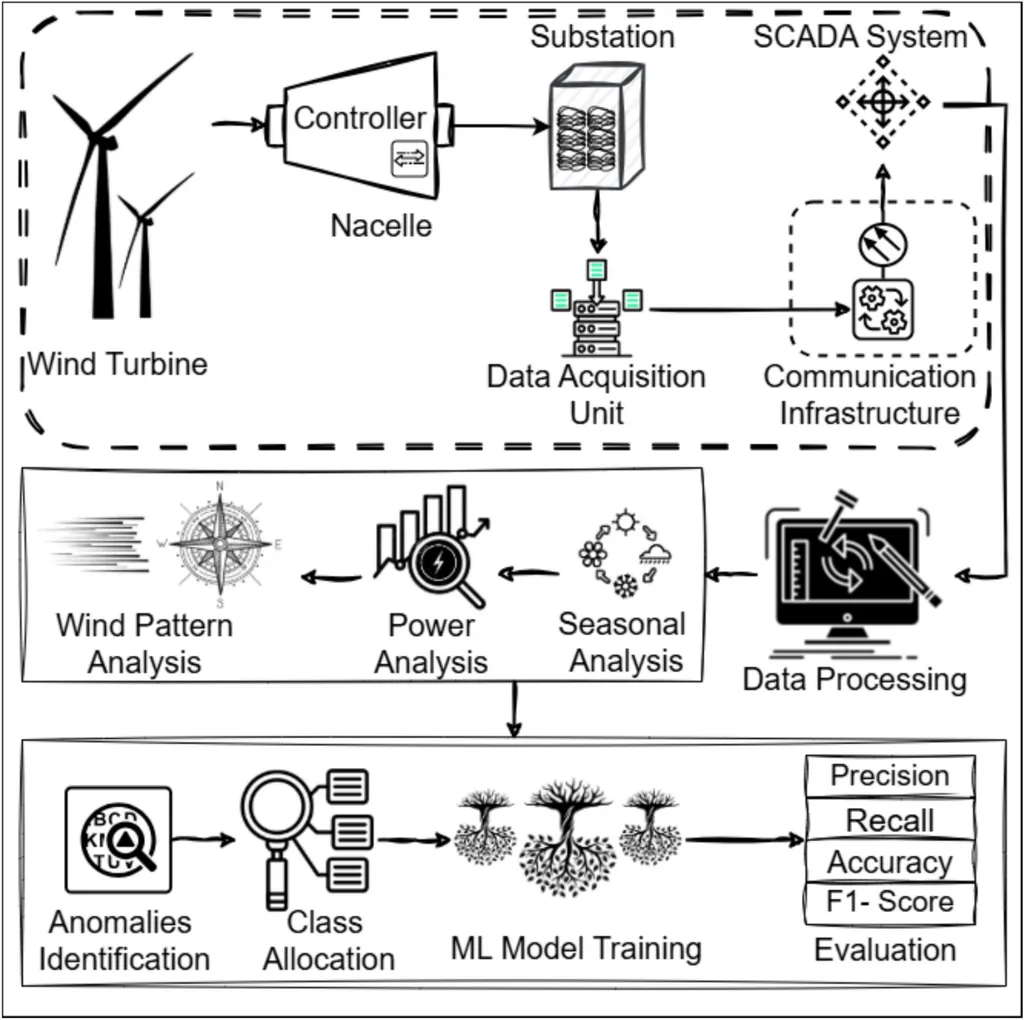
Researchers Khuram Naveed and Naveed ur Rehman from the University of Engineering and Technology, Peshawar, have developed a new method for fault diagnosis in machinery, with potential applications in the energy sector, particularly for wind turbines. Their work, published in the journal Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, focuses on analyzing multichannel machine vibration data to detect faults more accurately.
The researchers propose a fully multivariate generalization of a technique called multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis (MFDFA). This new method, termed FM-MFDFA, is designed to capture cross-channel dependencies and variance biases in multichannel vibration data, providing a more accurate characterization of the multiscale structure of these signals. To enhance the relevance of the features identified, the framework integrates multivariate variational mode decomposition (MVMD) to isolate fault-relevant components before applying FM-MFDFA.
The practical application of this research is significant for the energy industry, particularly in the maintenance of wind turbines. Wind turbine gearboxes are critical components that can fail due to various factors, leading to costly downtime and repairs. The proposed method can effectively distinguish between healthy and faulty machine states, even under noisy conditions, making it a valuable tool for predictive maintenance. By analyzing vibration data from multiple sensors, the FM-MFDFA method can detect early signs of faults, allowing for timely interventions and reducing the risk of catastrophic failures.
The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of their method using wind turbine gearbox data, showing that it outperforms conventional MFDFA approaches. This advancement in fault diagnosis can lead to more efficient and reliable operation of wind turbines, ultimately contributing to the stability and sustainability of the energy grid. The research highlights the importance of advanced data analysis techniques in improving the maintenance and performance of energy infrastructure.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.