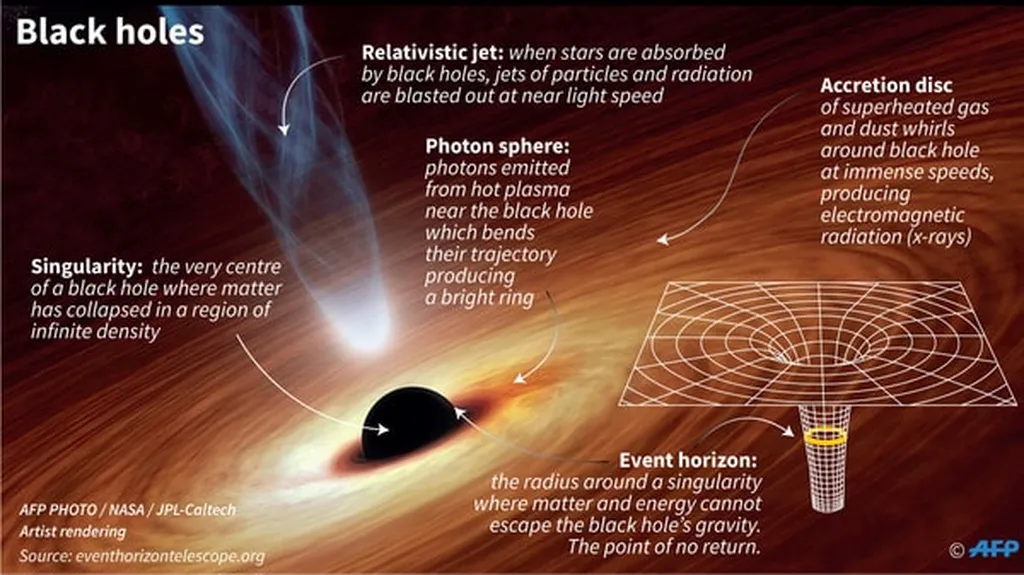
In the realm of theoretical physics, a team of researchers from various institutions, including Giorgos Anastasiou, Ignacio J. Araya, Avik Chakraborty, Cristóbal Corral, and Rodrigo Olea, has delved into the complexities of Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet AdS (Anti-de Sitter) gravity. Their work, published in the journal [Physical Review D](https://journals.aps.org/prd/), aims to better understand the behavior of certain types of black holes and the thermodynamic properties associated with them.
The researchers focused on the asymptotic analysis of the metric for generic solutions in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet AdS theory. They employed the Fefferman-Graham frame to solve the field equations and used standard holographic renormalization techniques to identify the counterterms that make the action finite, up to seven spacetime dimensions. For the specific case of six-dimensional space, they introduced an alternative formulation that allows for a fully covariant determination of the counterterms, based on the finiteness of conformal invariants. Importantly, they demonstrated that both schemes lead to the same holographic stress-energy tensor.
The study also examined the physical properties of six-dimensional topological Boulware-Deser black holes within the framework of Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet-AdS$_6$ gravity. These black holes have boundaries with nontrivial conformal features. By applying both renormalization prescriptions, the researchers were able to calculate finite asymptotic charges and correctly recover the black hole thermodynamics.
While this research is highly theoretical and abstract, it has potential implications for our understanding of gravity and black holes in higher-dimensional spaces. In the energy sector, such theoretical advancements can indirectly influence technologies that rely on a deep understanding of gravitational physics, such as satellite systems and advanced energy technologies that might harness gravitational effects. However, the direct practical applications for the energy industry are not immediately apparent, as this work is more foundational in nature.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.