Researchers from the Universitat Politècnica de València and the Instituto de Microelectrónica de Madrid have made a significant stride in solar cell technology. Their work focuses on improving the efficiency of solar cells by using a unique combination of materials and techniques.
The team, led by M. Sun and including R. Gómez, B. Damilano, J. M. Asensi, F. B. Naranjo, and S. Valdueza-Felip, has successfully demonstrated the first experimental use of Indium Nitride (InN) nanowire solar cells deposited by RF sputtering. This method is notable for its potential to reduce manufacturing costs and complexity. The researchers optimized the deposition of amorphous Silicon (a-Si) on Silicon (Si) substrates using DC sputtering, creating an amorphous material with a bandgap energy of 1.39 eV.
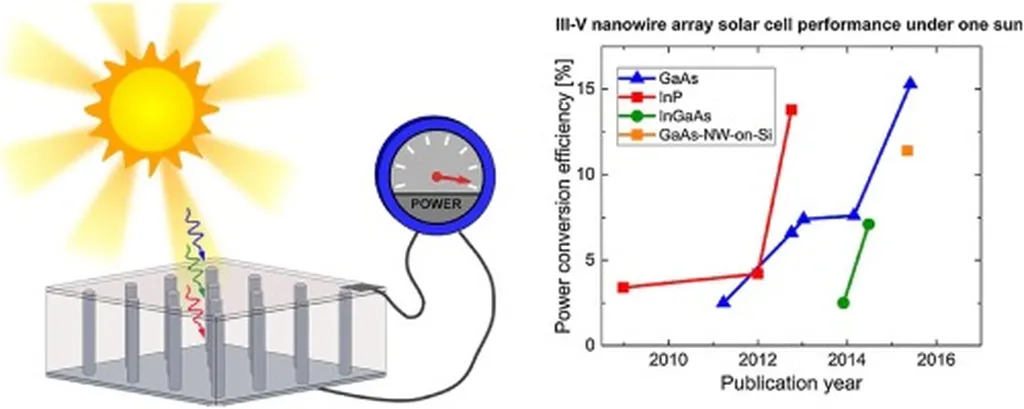
The study, published in the journal “Nano Energy,” investigated the impact of varying the thickness of the a-Si buffer layer (ranging from 0 to 25 nm) on the structural, morphological, electrical, and optical properties of InN nanowires on Si (100) substrates. The researchers found that using a 15-nm buffer layer significantly enhanced the photovoltaic performance of the n-InN/a-Si/p-Si nanowire heterojunction solar cells. These cells achieved a short-circuit current density of 17 mA/cm², an open-circuit voltage of 0.37 V, and a fill factor of 35.5%, resulting in a power-conversion efficiency of 2.3% under standard 1-sun (AM 1.5G) illumination.
The practical applications for the energy sector are promising. The combination of in-situ sputtered a-Si, which can serve as a potential passivation layer, and the light trapping enhancement by the nanostructured active layer, leads to an improvement in the photovoltaic efficiency of sputtered III-nitride devices. This advancement could contribute to more efficient and cost-effective solar cells, ultimately benefiting the renewable energy industry.
The research was published in the journal “Nano Energy.”
This article is based on research available at arXiv.