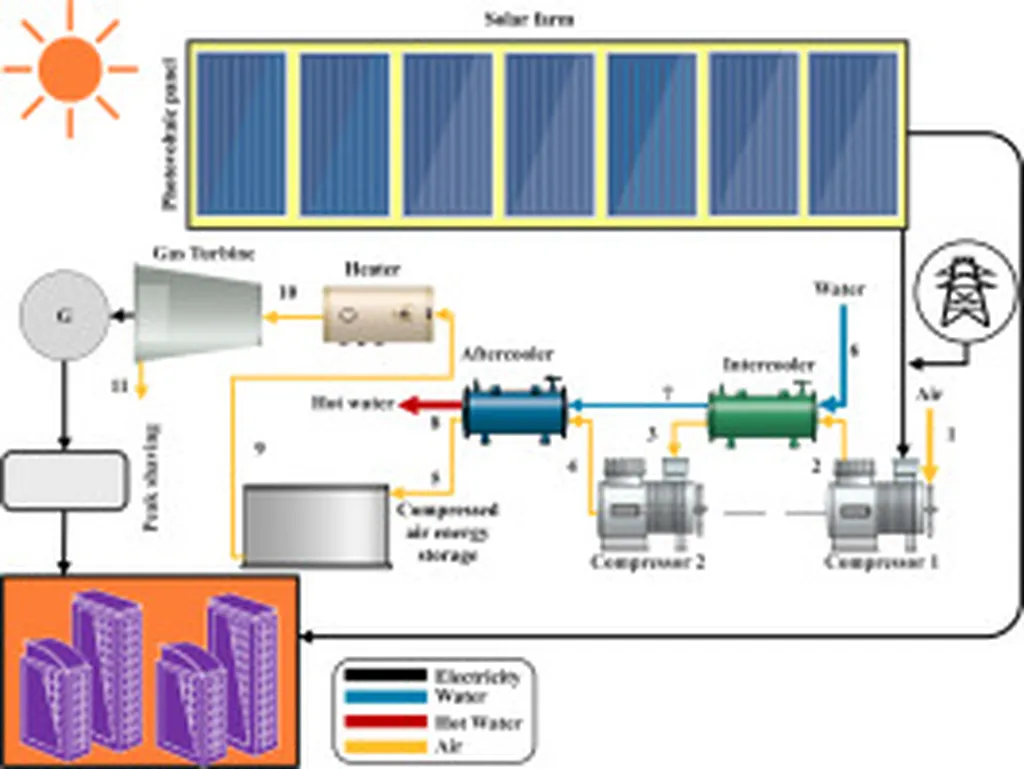
Researchers Vishal Kachhad, Amit Joshi, and Luigi Glielmo, affiliated with the University of Salerno in Italy, have published a study in the journal Applied Energy that explores how to optimize the use of solar power and battery storage systems within renewable energy communities (RECs). Their work aims to help individuals and communities make informed decisions about adopting renewable energy technologies.
The study focuses on determining the optimal sizes of photovoltaic (PV) systems and battery energy storage systems (BESS) for individual participants in RECs. The researchers considered various factors, including dynamic electricity pricing, solar irradiation levels, and financial aspects such as capital investment, operational and maintenance expenditures, replacement costs, and the efficiency of charging and discharging the BESS unit. To tackle this complex problem, they employed a mathematical optimization technique called Mixed-Integer Non-Linear Programming (MINLP), which helps find the best solution that maximizes the Net Present Value (NPV) for each participant.
One of the key innovations in this study is the use of daily representative signals for each season of the year to reduce simulation runtime. The researchers used the Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm (FISTA) to extract these representative signals, which were then used in the optimization problem to make the analysis more efficient and extend the planning horizon. This approach allows for a more practical and useful analysis, as it can be applied to real-world scenarios with longer time frames.
Another important aspect of the study is the introduction of fairness in the distribution of incentives among REC participants. The researchers applied the individual marginal contribution method to ensure that each member benefits equitably from their contribution to the REC. This approach promotes a more just and sustainable energy community.
To demonstrate the practical relevance of their ideas, the researchers conducted a simulation study using real demand data from five houses located in Roseto Valfortore, a small town in southern Italy. The results of the study provide valuable insights into how RECs can optimize the use of PV and BESS systems to maximize their benefits and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
In summary, this research offers a comprehensive approach to optimizing the use of renewable energy technologies within RECs. By considering various technical and financial factors, as well as promoting fairness in incentive distribution, the study provides a practical framework for individuals and communities to make informed decisions about adopting renewable energy. The findings of this study can be applied to real-world scenarios, helping to shape the future of sustainable energy and empowering RECs to play a more significant role in the energy transition.
Source: Kachhad, V., Joshi, A., & Glielmo, L. (2023). Techno-Economic Modelling and Component Sizing in Renewable Energy Communities: A Participant Perspective. Applied Energy, 335, 120608.
This article is based on research available at arXiv.