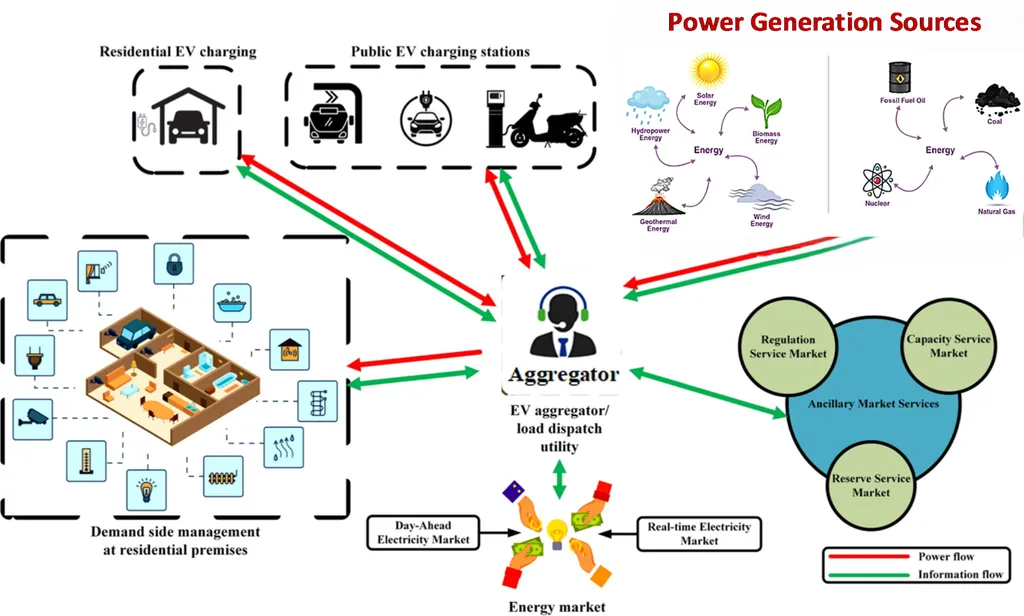
In a significant stride towards optimizing power networks, researchers have introduced a decentralized demand response (DR) framework that tackles the persistent challenges of uncertainties in energy generation and consumption. The study, published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, offers a novel approach to energy management that could reshape the future of the power industry.
Lead author Alireza Norouzpour Shahrbejari, whose affiliation is not specified, and his team have developed a multi-objective energy management strategy that integrates advanced DR techniques with a robust framework designed to handle uncertain conditions. “Our approach not only considers the environmental impacts but also evaluates the long-term economic implications, providing a comprehensive solution for the power industry,” Norouzpour Shahrbejari explained.
The research focuses on networks with distributed generating resources, including wind turbines, microturbines, photovoltaics, energy storage systems, and diesel generators. These resources are controlled hourly based on load fluctuations, requiring both distributed energy generation and DR to variations in demand to ensure system reliability.
One of the key aspects of this study is the incentive-based participation of consumers, who play a crucial role in optimizing energy usage. “By involving consumers in the process, we can achieve a more balanced and efficient energy consumption pattern,” Norouzpour Shahrbejari added.
The researchers employed a stochastic approach to obtain the best outcomes in reducing generation and purchasing costs in power grids. The findings are promising, with improvements in network efficiency and cost reduction. The study reports a 15.62% decrease in voltage deviation, a 37.08% reduction in load demand, a 62.05% decrease in active losses, an 81.25% reduction in reactive losses, and a 33-45% reduction in Expected Energy Not Supplied (EENS).
The implications of this research are far-reaching. By integrating stochastic techniques to manage uncertainties and variable conditions, the proposed method could significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of power networks. This could lead to substantial cost savings for energy providers and consumers alike, while also reducing the environmental impact of power generation.
As the power industry continues to evolve, the need for innovative solutions to manage uncertainties and optimize energy consumption becomes increasingly critical. This research, published in PLOS ONE, offers a glimpse into the future of energy management, where decentralized DR frameworks and advanced stochastic techniques could play a pivotal role.
The study not only highlights the potential for improved network efficiency but also underscores the importance of consumer participation in achieving optimal energy management. As Norouzpour Shahrbejari noted, “The involvement of consumers is not just beneficial but essential for creating a sustainable and efficient energy ecosystem.”
In the coming years, the integration of such advanced techniques into existing power networks could pave the way for a more resilient and cost-effective energy infrastructure. The research by Norouzpour Shahrbejari and his team represents a significant step forward in this direction, offering valuable insights and practical solutions for the energy sector.